DRV8837 Low-Voltage H-Bridge Motor Driver
The DRV8837 is a low-cost N channel MOSFET-based H bridge DC motor driver which is capable of driving a DC motor in Bi-direction or similar inductive loads. This IC has an internal charge pump which generates the required gate drive voltage. This motor driver IC can deliver up to a 1.8A peak current. It has two inputs to control the direction of the motor also we can use these inputs to change the rotation speed by providing PWM signals. It can be operated with a 0-11v power supply. The DRV8897 Offers short circuit, under voltage, overcurrent, and over temperature protections. This IC is available in an 8-pin WSON package.
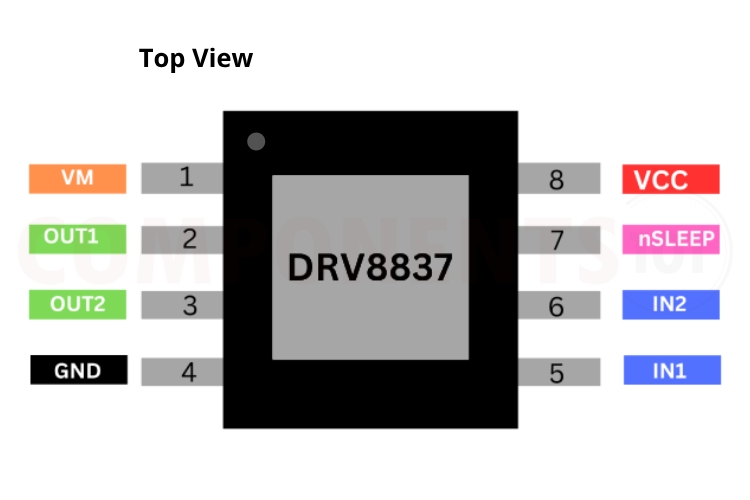
DRV8837 Pinout Configuration
Here are the pinout details for DRV8837.
| PIN | NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| 1 | VM | Motor power supply |
| 2 | OUT1 | Motor output |
| 3 | OUT2 | Motor output |
| 4 | GND | ground |
| 5 | IN2 | Input 2 |
| 6 | IN1 | Input 1 |
| 7 | nSLEEP | SLEEP mode input |
| 8 | VCC | Logic power supply |
Features of DRV8837
DRV8837 bi-directional DC motor Driver has the following key features:
- Low MOSFET On-Resistance: HS + LS 280 mΩ
- 1.8-A Maximum Drive Current
- Separate Motor and Logic Supply Pins: – Motor VM: 0 to 11 V – Logic VCC: 1.8 to 7 V
- PWM Interface
- Low-Power Sleep Mode With 120-nA Maximum Sleep Current – nSLEEP pin
- Small Package and Footprint – 8-Pin WSON With Thermal Pad – 2.0 × 2.0 mm
- Protection Features – VCC Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) – Overcurrent Protection (OCP) – Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
Manufacturers of DRV8837:
The DRV8837 is manufactured by Texas Instruments. There are no alternative manufacturers for the same part number as of the date of writing this article.
DRV8837 Equivalents
If you are looking for an equivalent or replacement for DRV8837, you can use DRV8837C or DRV8838, but keep in mind that DRV8837C is limited to 1A. Also, DRV8837 and DRV8837C uses two PWM inputs as controls while DRV8838 uses phase input and enable input as controls.
DRV8837 Alternatives
If you are looking for an alternative for DRV8837 you can look at the other ICs from these.
L293D, L298, TB6612FNG, DRV8833, MAX1508, TA6586, DRV8871, MAX1919, L9110.
Note: Complete technical details can be found in the DRV8837 datasheet at this page’s end.
DRV8837 Schematics
The following image shows the typical circuit diagram for DRV8837.

The above circuit diagram shows how to connect and drive a motor using DRV8837. In this circuit, the motor is connected to pin OUT1 and pin OUT2. The ground is connected to the ground of the circuit. VM is connected to the motor/load power supply. This voltage depends on motor voltage, we can set this according to the motor voltage. VCC is connected to the logic power supply input. Here we added the 0.1uf bypass capacitor parallel with the motor supply voltage and logic supply voltage. To control the direction of the motor in the circuit we have connected the input pins to the output pins of a microcontroller. We can use any microcontroller here. You can control the motor according to this truth table. We can control the motor speed by connecting the inputs to a PWM signal. We can use the nSLEEP pin to control the IC.
| nSLEEP | IN1 | IN2 | OUT1 | OUT2 | FUNCTION (DC MOTOR) |
| 0 | X | X | Z | Z | Coast |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Z | Z | Coast |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | L | H | Reverse |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | H | L | Forward |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | L | L | Brake |
Having trouble with DRV8837?
My circuit is resetting when I turn on the circuit?
It might be due to the voltage spike/load drawing more current than the rated range, so check the motor supply voltage and also try to add a capacitor parallel to the motor.
Why is my circuit not working?
1. Check all connections, and make sure everything is connected properly.
2. Check the motor voltage and current. Make sure that the rating is in the range of IC rating
3. Should connect the ground of the motor power supply and the logic circuit is commonly connected
The IC gets very hot and automatically turns off:
- Overloading: The motor driver IC may be driving a motor that draws more current than the IC can handle. Check the datasheet for the maximum current rating of the motor
- Voltage Spikes: If there are voltage spikes or transients in the motor circuit, it could cause the IC to overheat. Adding capacitors to suppress these spikes can help protect the IC.
- Poor Heat Dissipation: The IC may not be dissipating heat efficiently. Make sure the IC is operating below 100 degrees Celsius
- The motor is jerking: make sure the voltage and current rating of the motor match with the IC maximum parameters. Add .1uf capacitor parallel to the motor pins to reduce the noise.
How to do DRV8837 Arduino Interfacing?
For controlling the DRV8837 you will need two GPIO pins. Connect the inputs of DRV8837 to these pins, set them as output and by changing the state of these pins you can control the DRV8837 and the motor connected to it. You can refer to the truth table given above.
Is a heat sink necessary for the working of DRV8837?
No. For most applications, the DRV8837 can operate without a heat sink within its specified operating conditions.
What is the difference between DRV8837 and DRV8837C?
The DRV8837 is capable of handling current up to 1.8A while the DRV8837C is limited to 1A.
What is the difference between DRV8837DSGR and DRV8837DSGT?
Both are the same the only difference is that DRV8837DSGR comes in a 3000QTY pack while DRV8837DSGT comes in a 250QTY pack.
Design Choices to be Considered with DRV8871
Power Supply Recommendations
Having appropriate local bulk capacitance is an important factor in motor-drive system design. It is generally beneficial to have more bulk capacitance, while the disadvantages are increased cost and physical size. The amount of local capacitance needed depends on a variety of factors, including:
- The highest current required by the motor system
- The power-supply capacitance and ability to source current
- The amount of parasitic inductance between the power supply and motor system
- The acceptable voltage ripple
- The type of motor used (brushed dc, brushless dc, stepper)
- The motor braking method
The inductance between the power supply and the motor drive system limits the rate at which current can change from the power supply. If the local bulk capacitance is too small, the system responds to excessive current demands or dumps from the motor with a change in voltage. When adequate bulk capacitance is used, the motor voltage remains stable and high current can be quickly supplied. The data sheet generally provides a recommended value, but system-level testing is required to determine the appropriate size of the bulk capacitor.
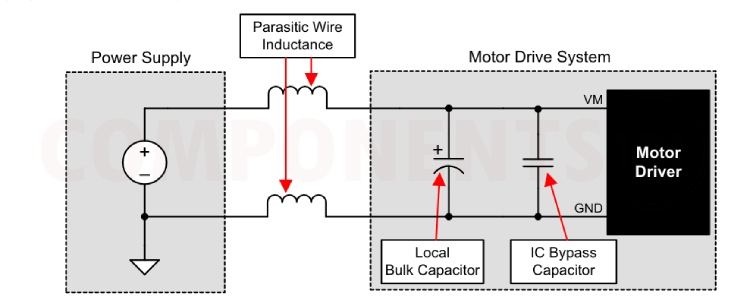
The voltage rating for bulk capacitors should be higher than the operating voltage, to provide the margin for cases when the motor transfers energy to the supply.
Layout Guidelines
The VM and VCC pins should be bypassed to GND using low-ESR ceramic bypass capacitors with a recommended value of 0.1 µF rated for VM and VCC. These capacitors should be placed as close to the VM and VCC pins as possible with a thick trace or ground plane connection to the device's GND pin.
Layout Example

Power Dissipation
Power dissipation in the DRV8837 is dominated by the power dissipated in the output FET resistance, or rDS(on). Use the Equation to estimate the average power dissipation when running a stepper motor.
2 P r (I ) TOT DS(on) OUT(RMS) = ´ (1) where
- PTOT is the total power dissipation
- rDS(on) is the resistance of the HS plus LS FETs
- IOUT(RMS) is the RMS or DC output current being supplied to the load The maximum amount of power that can be dissipated in the device is dependent on ambient temperature and heatsinking.
Applications of DRV8837
- Robotics
- printers
- Motorised Vehicles
- Toys
- Solar Tracking System
- DIY Projects
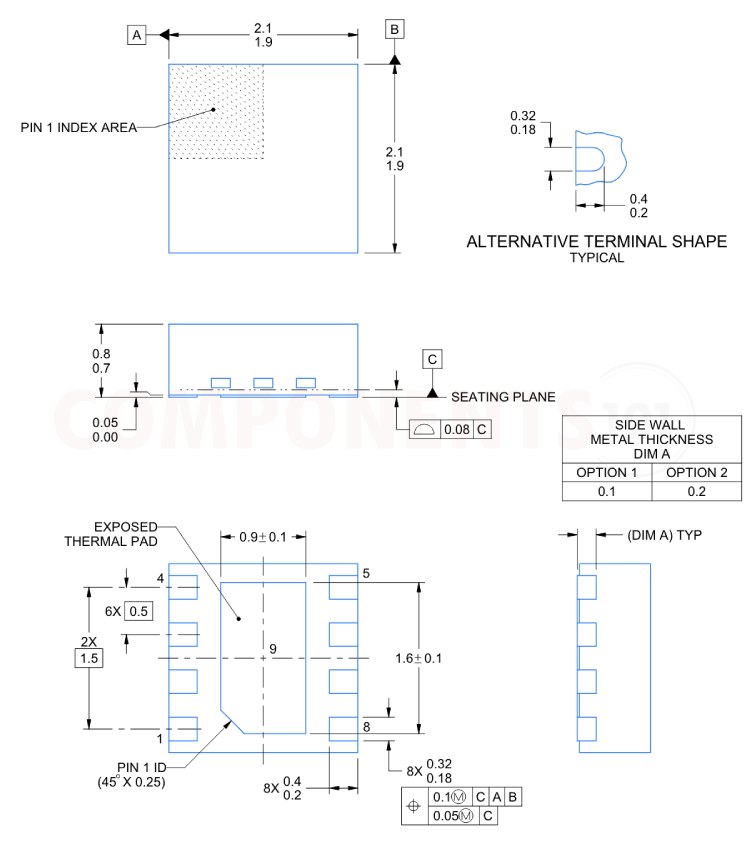
DRV8837 Footprint Information and Dimensions
Here you can find the mechanical drawings of DRV8837 along with its dimensions. The dimensions can be used to create custom footprints of the module and be used for PCB or CAD modelling.