6N135 High Speed Optocoupler
The 6N135 is a high speed Optocoupler with Transistor output. It can switch at a speed of 1 Mbit/s with Bandwidth of 2MHz. It is TTL compatible with open collector output commonly used in Power supply circuits like inverter or in Data transfer circuits as logic isolators.
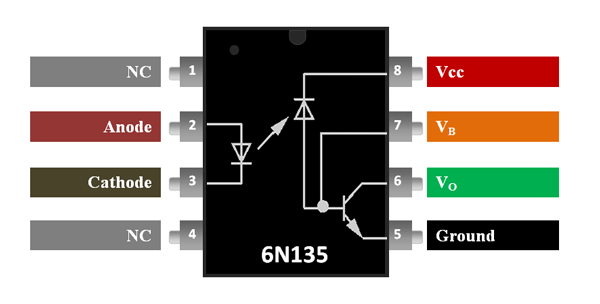
6N135 Pin Description
|
Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|
1 |
NC |
No Connection - Cannot be used |
|
2 |
Anode (A) |
Anode pin of the IR LED. Connected to logic input |
|
3 |
Cathode (C) |
Cathode pin of the IR LED |
|
4 |
NC |
No Connection - Cannot be used |
|
5 |
Ground |
Ground pin of the IC |
|
6 |
Output (VO) |
Isolated Output pin of the Optocoupler |
|
7 |
Base (VB) |
By default it is enabled through a pull-up resistor. |
|
8 |
Vcc |
Powers the IC |
6N135 features and specifications
- High Speed Optocoupler (1Mbit/s)
- Isolation Voltage: 2500 Vrms
- Maximum Supply voltage: 15V
- Input forward voltage: 1.3V to 1.9V
- Emitter base Voltage: 5V
- Output sink current: 8mA (max)
- Available as 6-pin DIP and SMD Packages.
Note: More details can be found at the 6N135 optocoupler datasheet which is available for download at the end of this page.
6N135 Equivalent
HCPL4503M
Alternatives Opto-couplers
MOC3021 (Zero-crossing), MCT2E (non-Zero transistor), MOC3041 (Non-Zero Cross TRIAC), FOD3180 (High-Speed MOSFET), PC817, 4N25, 6N137
Where to use 6N135 Optocoupler
The 6N135 is a High Speed Optocoupler or Optoisolator. As we know the term Optocoupler/Optoisolater means we use light to indirectly couple (isolate) two sets of circuits. The speciality of 6N135 is that it has a high speed LED and hence can switch at 1Mbit/sec the output of the coupler is a TTL logic transistor making it easy to interface with other circuits.
The 6N135 is very similar to 6N137, the major difference is that 6N135 has transistor output and 6N137 has NAND output Enabling it to have high switching speed of 10Mbit/sec compared with the 1Mbit/sec of 6N135.
The maximum operating voltage of 6N135 is 15V and the transistor has an output current of 8mA with a peak of 16mA making it suitable to drive medium level loads. If you looking for some high voltage AC/DC switching try the MOC3021. Apart from that the IC also has an Enable pin which comes in handy while designing a strobe circuit for your camera flash.
So if you are looking for a high speed optocoupler for some digital applications like data conversion or noise elimination then this IC might be of interest to you.
How to use 6N135 Optocoupler
Even though 6N135 is capable of working with both AC and DC it is commonly used with Digital circuits and works with 5V as supply voltage. A typical application circuit for 6N135 from data sheet is shown below
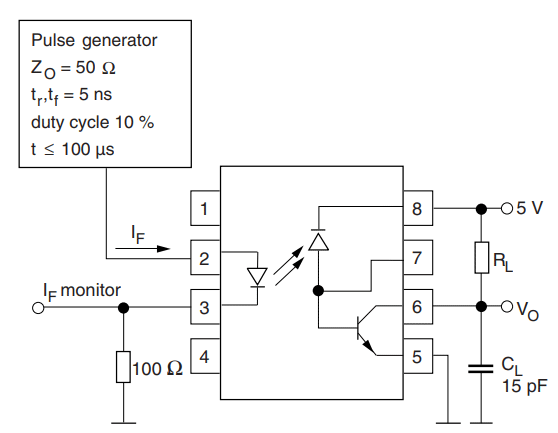
The Capacitor 0.1uF is a bypass capacitor across the Supply rail. The input signal should has an impedance of minimum 50 ohms with rise time and falls of 5nS of greater for the IC to respond. The input signal can be probed (if required) on pin 3 and the pull down resistor 100Ω is optional and can be used only if you are connecting the signal to scope.
As told earlier the output (pin 6) is an open drain transistor and hence it can either sink current or remain floating. So to avoid floating we should use a pull up resistor RL, the value of RL can be between 330 ohm to 4K depending upon the load connected.
The pin 7 is the Enable pin, this pin has an in-built pull up resistor hence by default the IC is enabled when powered. When connected to ground it will disable the output. The pin can be put into use to create strobe circuits etc.. The below truth table will help you understand the working of Enable pin.
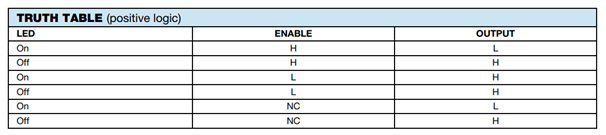
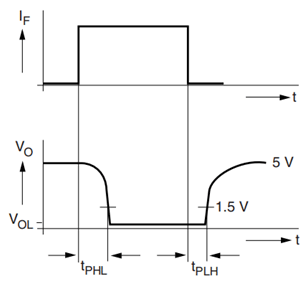
Since the output is of open drain type, note that when the input is high the output will be low and vice versa. Since the IC is commonly used for fast switching another thing to consider is the propagation delay. When the input is logic on the output turn off only after (TPHL) and when the input is logic off the output turns on only after (TPLH). The same can be understood with the below switching diagram.
Applications
- Camera Strode lights
- High speed ADC and DAC
- Fibre/optic communication
- Noise isolation circuits
- Input / Output isolation circuits
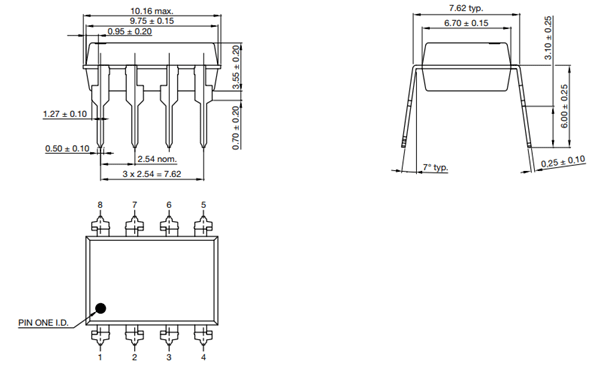
2D-Model