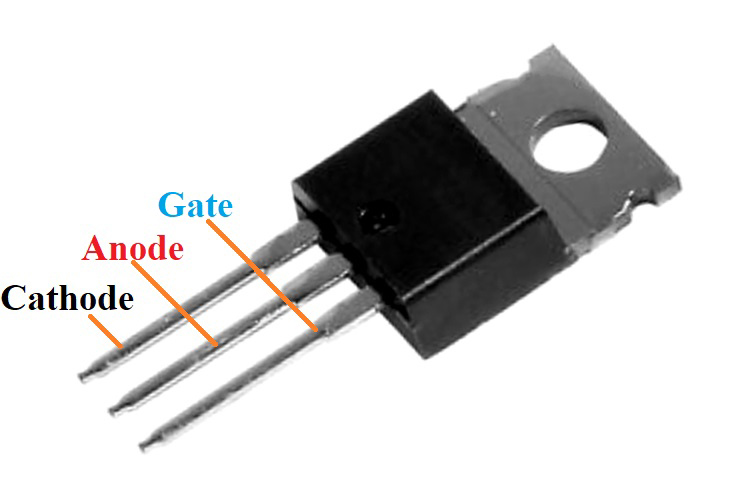
FQD2N60C Power MOSFET
The FQD2N60C is a switching MOSFET from Fairchild Semiconductor that features a high breakdown voltage optimized for primary side switching in DC-DC converters.
Pin Description of FQD2N60C
|
Pin No: |
Pin Name: |
Pin Description: |
|
1 |
GATE |
Gate terminal that controls conduction |
|
2 |
DRAIN |
Current (conventional) ‘drain’ into this terminal |
|
3 |
SOURCE |
Connected to ground, ‘source’ of electrons |
|
TAB |
DRAIN |
The metal tab is internally connected to the drain |
Features of IRFB4115
- N-channel power MOSFET
- Very high breakdown voltage: 600V
- Drain current: 1.9A
- On resistance: 3.6Ω typical
- Gate threshold voltage: 2V to 4V
- Rise and fall times 60ns and 66ns respectively
- Comes in an IPAK and DPAK packages
Note: Complete technical details can be found in the FQD2N60C Datasheet linked at the bottom of the page.
Alternatives for IRFB4115: STP5NK60Z, FCA20N60, NDF10N60ZG
Other N-Channel MOSFETs: IRF3205, IRF540N, 80N60
Where to Use the FQD2N60C
The FQD2N60C is a high voltage power MOSFET with a relatively high on the resistance of 3.6Ω. While it may not excel at high power switching, it is excellent for high voltage applications, where current is not an important factor. For example, it can be used as a primary side switch for a DC-DC converter that runs off the mains. Here it is more efficient than an NPN BJT, which has a constant voltage drop of 0.7V even when switching 100mA, whereas the FQD2N60C has only 3.6V drop, halving the losses. It can also be used as a high voltage motor driver.
How to Use the IRFB4115
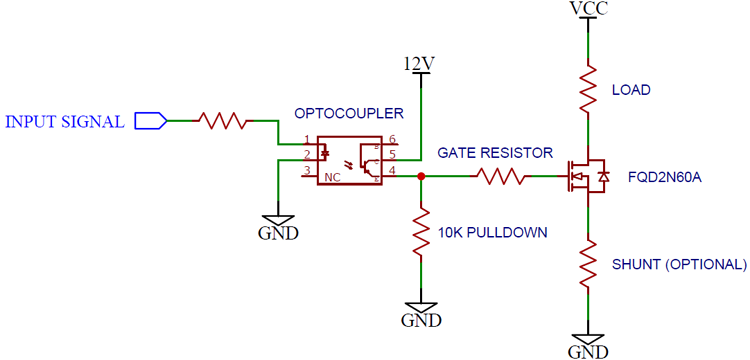
Since the FQD2N60C is meant for high voltage applications, special care must be taken to prevent device damage. An optocoupler can be used to drive the gate since the gate capacitance is low (180pF), so it does not require much charge to turn on completely. A TVS Diode could be added to the gate to prevent overvoltage, as shown in FIG.1.
Applications Of FQD2N60C
- High-efficiency switched-mode power supplies
- Active power factor correction
- Electronic lamp ballasts based on half-bridge topology