Arduino Uno
Arduino Uno is a popular microcontroller development board based on 8-bit ATmega328P microcontroller. Along with ATmega328P MCU IC, it consists of other components such as crystal oscillator, serial communication, voltage regulator, etc. to support the microcontroller. This article explores the Arduino UNO pin diagram in detail along with basics on how to use this board and upload your first code.
Please note that this article discusses the popular Arduino UNO R3 development board and not the latest Arduino UNO R4 board which was launched recently. If you are new you can also check out our article on Arduino UNO R3 vs Arduino Arduino UNO R4 to understand the differences between these two boards.
Arduino Uno Pinout Configuration
|
Pin Category |
Pin Name |
Pin Description |
|
Power |
Vin, 3.3V, 5V, GND |
Vin: Input voltage to Arduino when using an external power source. 5V: Regulated power supply used to power microcontroller and other components on the board. 3.3V: 3.3V supply generated by on-board voltage regulator. Maximum current draw is 50mA. GND: ground pins. |
|
Reset |
Reset |
Resets the microcontroller. |
|
Analog Pins |
A0 – A5 |
Used to provide analog input in the range of 0-5V |
|
Input/Output Pins |
Digital Pins 0 - 13 |
Can be used as input or output pins. |
|
Serial |
0(Rx), 1(Tx) |
Used to receive and transmit TTL serial data. |
|
External Interrupts |
2, 3 |
To trigger an interrupt. |
|
PWM |
3, 5, 6, 9, 11 |
Provides 8-bit PWM output. |
|
SPI |
10 (SS), 11 (MOSI), 12 (MISO) and 13 (SCK) |
Used for SPI communication. |
|
Inbuilt LED |
13 |
To turn on the inbuilt LED. |
|
TWI |
A4 (SDA), A5 (SCA) |
Used for TWI communication. |
|
AREF |
AREF |
To provide reference voltage for input voltage. |
Arduino Uno Technical Specifications
|
Microcontroller |
ATmega328P – 8 bit AVR family microcontroller |
|
Operating Voltage |
5V |
|
Recommended Input Voltage |
7-12V |
|
Input Voltage Limits |
6-20V |
|
Analog Input Pins |
6 (A0 – A5) |
|
Digital I/O Pins |
14 (Out of which 6 provide PWM output) |
|
DC Current on I/O Pins |
40 mA |
|
DC Current on 3.3V Pin |
50 mA |
|
Flash Memory |
32 KB (0.5 KB is used for Bootloader) |
|
SRAM |
2 KB |
|
EEPROM |
1 KB |
|
Frequency (Clock Speed) |
16 MHz |
Note: Complete technical information can be found in the Arduino UNO Datasheet, linked at the bottom of this page.
Other Arduino Boards
Arduino Nano, Arduino Pro Mini, Arduino Mega, Arduino Due, Arduino MKR1000 Wi-Fi Board, Arduino Leonardo
Overview
Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board based on 8-bit ATmega328P microcontroller. Along with ATmega328P, it consists other components such as crystal oscillator, serial communication, voltage regulator, etc. to support the microcontroller. Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (out of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog input pins, a USB connection, A Power barrel jack, an ICSP header and a reset button.
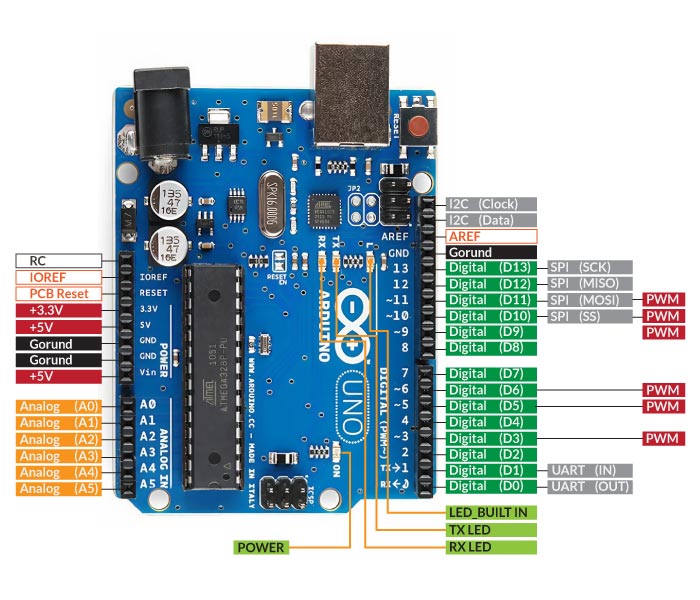
Arduino UNO Pin Layout Overview
The Arduino UNO pin layout is organized into distinct categories, including Power Pins, Digital Pins, Analog Pins, and Special Function Pins. Each category plays a specific role in enabling the functionality of the board. The Arduino UNO pinouts available under each category is shown in the image below
Now, lets understand the function of each pin under in detail under different category
Power Pins
Power pins are essential for operating the board and connected devices. The main pins include:
- VIN: Accepts external power sources (7-12V).
- 5V and 3.3V: Provide regulated voltage outputs for peripherals.
- GND (Ground): Completes the circuit.
- IOREF: Supplies a voltage reference for I/O pins.
Tip: Always verify the voltage compatibility of connected components to avoid damage.
Digital Pins (0-13)
The Arduino UNO has 14 digital pins that can function as inputs or outputs.
- Pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX): Reserved for serial communication.
- Pins 2-13: General-purpose I/O pins.
- PWM Pins (3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11): Support Pulse Width Modulation, ideal for applications like controlling motors and dimming LEDs.
Use functions like pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() to interact with these pins.
Analog Pins (A0-A5)
Analog pins allow reading continuous voltage signals, often from sensors.
- Resolution: 10-bit (0 to 1023 range).
- Flexibility: Can also function as digital I/O pins when required.
Special Function Pins
- Reset Pin: Resets the board when triggered.
- AREF: Used to provide an external voltage reference for analog inputs.
- Serial Pins (RX/TX): Facilitate UART communication for serial data exchange.
ICSP Header
The ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) header allows direct programming of the microcontroller or connecting additional peripherals.
- MISO (Master-In-Slave-Out): Receives data from peripherals.
- MOSI (Master-Out-Slave-In): Sends data to peripherals.
- SCK (Serial Clock): Synchronizes data transfer.
Communication Pins
- I2C Pins: SCL (Clock line) and SDA (Data line) are located on A5 and A4, respectively.
- SPI Pins: Share functionality with the ICSP header (MISO, MOSI, and SCK).
- UART Pins: TX (Pin 1) and RX (Pin 0) handle serial communication.
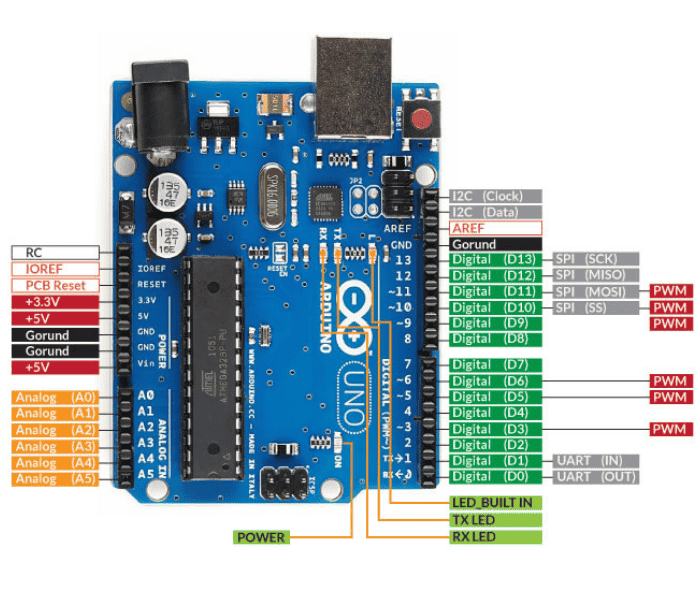
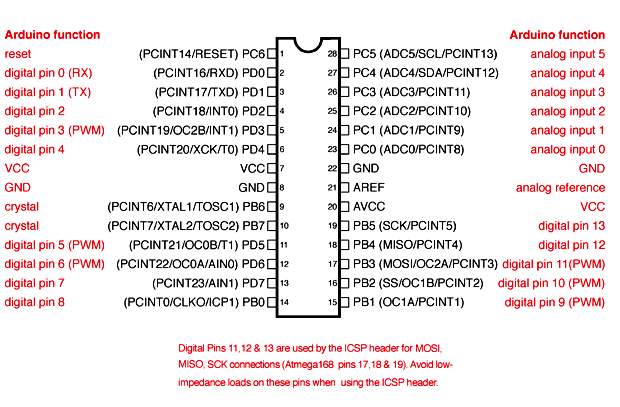
Arduino Uno to ATmega328 Pin Mapping
When ATmega328 chip is used in place of Arduino Uno, or vice versa, the image below shows the pin mapping between the two.
Software (Arduino IDE)
Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment) is required to program the Arduino Uno board. Download it from here.
Programming Arduino
Once arduino IDE is installed on the computer, connect the board with computer using USB cable. Now open the arduino IDE and choose the correct board by selecting Tools>Boards>Arduino/Genuino Uno, and choose the correct Port by selecting Tools>Port. Arduino Uno is programmed using Arduino programming language based on Wiring. To get it started with Arduino Uno board and blink the built-in LED, load the example code by selecting Files>Examples>Basics>Blink. Once the example code (also shown below) is loaded into your IDE, click on the ‘upload’ button given on the top bar. Once the upload is finished, you should see the Arduino’s built-in LED blinking. Below is the example code for blinking:
// the setup function runs once when you press reset or power the board
void setup() {
// initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output.
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
Applications
- Prototyping of Electronics Products and Systems
- Multiple DIY Arduino Projects.
- Easy to use for beginner level DIYers and makers.
- Projects requiring Multiple I/O interfaces and communications.
Commonly Asked Question when working with Arduino UNO
Q1. What is the function of PWM pins on Arduino UNO?
PWM pins generate variable output signals for tasks like motor control and dimming LEDs.
Q2. Can I use analog pins as digital pins?
Yes, analog pins (A0-A5) can be configured as digital I/O pins.
Q3. What is the role of the ICSP header?
It allows direct programming of the microcontroller or connecting advanced peripherals.
Q4. What happens if I supply more than 5V to an I/O pin?
Excess voltage can permanently damage the microcontroller.
Q5. Are all digital pins PWM-capable?
No, only pins 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11 support PWM.
Q6. How do I power the Arduino UNO?
You can use the USB port, VIN pin, or DC power jack.
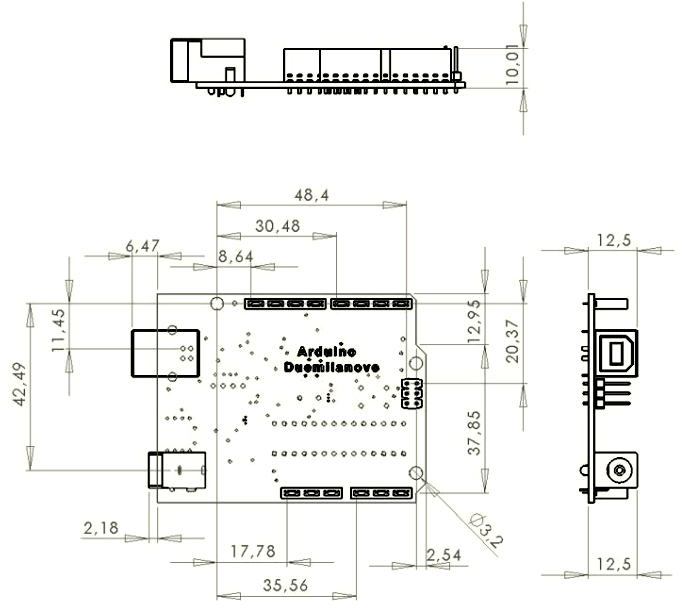
2D Model and Dimensions