PIC18F2550 Microcontroller
‘PIC’ is the popular microcontroller series from MICROCHIP and PIC18F2550 is one of the popular microcontroller from ‘PIC18F’ family. PIC18F2550 is a High-Performance, Enhanced flash, USB Microcontroller with NANO-Watt-Technology. This is an 8-bit microcontroller popular among makers and engineers due to its features and low cost. PIC18F2550 comes in various packages like DIP, QPF and QPN and can be selected according to the project requirement.
PIC18F2550 Pinout Configuration
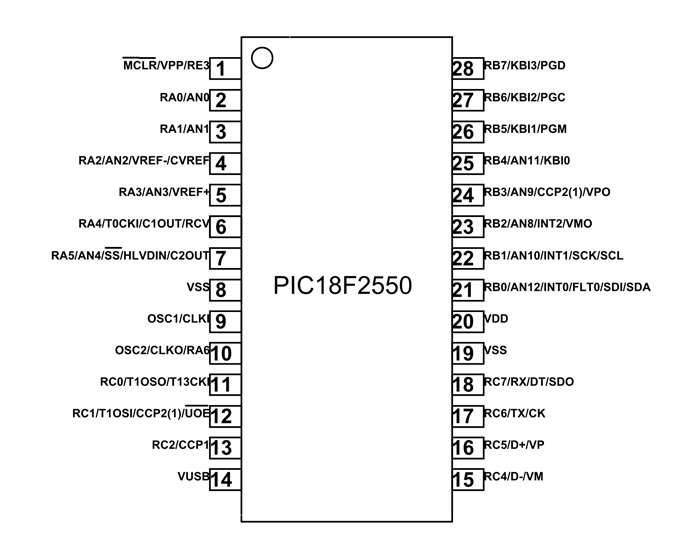
It is a 28 pin IC as shown in PIC18F2550 pin diagram. There are so many features for a controller the manufacturer cannot provide I/O pins for each of them. So many pins of controller have multiple features. These features are disabled by default and can be enabled through programming. We will briefly describe functions of each pin below.
|
Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|
1 |
MCLR/VPP/RE3 |
MCLR: Master Clear(RESET) Input VPP:programming voltage input RE3: I/O pin of PORTE, PIN 3 |
|
2 |
RA0/AN0 |
RA0: I/O pin of PORTA, PIN 0 AN0: Analog input 0 |
|
3 |
RA1/AN1 |
RA1: I/O pin of PORTA, PIN 1 AN1: Analog input 1 |
|
4 |
RA2/AN2/VREF-/CVREF |
RA2: I/O pin of PORTA, PIN 2 AN2: Analog input 2 VREF-: A/D reference voltage (low) input CVREF: Analog comparator reference output |
|
5 |
RA3/AN3/VREF+ |
RA3: I/O pin of PORTA, PIN 3 AN3: Analog input3 VREF+: A/D reference voltage (high) input |
|
6 |
RA4/T0CKI/C1OUT/RCV |
RA4: I/O pin of PORTA, PIN 4 T0CKI: Timer0 external clock input C1OUT: Comparator 1 output RCV:External USB transceiver RCV input |
|
7 |
RA5/AN4/SS/HLVDIN/C2OUT |
RA5: I/O pin of PORTA, PIN 5 AN4: Analog input 4 SS: SPI slave select input HLDVIN: High/Low-Voltage Detect input C2OUT: Comparator 2 output |
|
8 |
VSS |
Ground |
|
9 |
OSC1/CLKI |
OSC1:Oscillator pin 1 CLKI: External clock source input |
|
10 |
OSC2/CLKO/RA6 |
OSC2: Oscillator pin 2 CLKO: clock source output RA6: I/O pin of PORTA, PIN 6 |
|
11 |
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI |
RC0: I/O pin of PORTC, PIN 0 T1OSO :Timer1 oscillator output T13CKI: Timer1/Timer3 external clock input |
|
12 |
RC1/T1OSI/CCP2/UOE |
RC1: I/O pin of PORTC, PIN 1 T1OSI: Timer1 oscillator input CCP2:Capture 2 input/Compare 2 output/PWM2 output UOE: External USB transceiver OE output |
|
13 |
RC2/CCP1 |
RC2: I/O pin of PORTC, PIN 2 CCP1: Capture 1 input/Compare 1 output/PWM1 output. |
|
14 |
VUSB |
VUSB:Internal USB 3.3V voltage regulator output |
|
15 |
RC4/D-/VM |
RC4: I/O pin of PORTC, PIN 4 D-: USB differential minus line (input/output) VM: External USB transceiver VM input |
|
16 |
RC5/D+/VP |
RC5: I/O pin of PORTC, PIN 5 D+: USB differential plus line (input/output). VP: External USB transceiver VP input |
|
17 |
RC6/TX/CK |
RC6: I/O pin of PORTC, PIN 6 TX: EUSART asynchronous transmit CK: EUSART synchronous clock (see RX/DT). |
|
18 |
RC7/RX/DT/SDO |
RC7: I/O pin of PORTC, PIN 7 RX: EUSART asynchronous receive DT: EUSART synchronous data (see TX/CK). SDO: SPI data out |
|
19 |
VSS |
Ground |
|
20 |
VDD |
Positive Power Supply (+5V) |
|
21 |
RB0/AN12/INT0/FLT0/SDI/SDA |
RB0: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 0 AN12: Analog input 12 INT0: External interrupt 0 FLT0: Enhanced PWM Fault input (ECCP1 module) SDI: SPI data in SDA: I2C data I/O |
|
22 |
RB1/AN10/INT1/SCK/SCL |
RB1: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 1 AN10: Analog input 10 INT1: External interrupt 1 SCK: Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI mode SCL: Synchronous serial clock input/output for I2C mode |
|
23 |
RB2/AN8/INT2/VMO |
RB2: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 2 AN8: Analog input 8 INT2: External interrupt 2 VMO: External USB transceiver VMO output |
|
24 |
RB3/AN9/CCP2/VPO |
RB3: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 3 AN9: Analog input 9 CCP2: Capture 2 input/Compare 2 output/PWM2 output VPO: External USB transceiver VPO output |
|
25 |
RB4/AN11/KBI0 |
RB4: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 4 AN11: Analog input 11 KBI0: Interrupt-on-change pin |
|
26 |
RB5/KBI1/PGM |
RB5: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 5 KBI1: Interrupt-on-change pin PGM: Low-Voltage ICSP Programming enable pin |
|
27 |
RB6/KBI2/PGC |
RB6: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 6 KBI2: Interrupt-on-change pin PGC: In-Circuit Debugger and ICSP programming clock pin. |
|
28 |
RB7/KBI3/PGD |
RB7: I/O pin of PORTB, PIN 7 KBI3: Interrupt-on-change pin PGD: In-Circuit Debugger and ICSP programming data pin. |
PIC18F2550 Microcontroller Features
|
PIC18F2550 – Simplified Features |
|
|
CPU |
8-bit |
|
Total Number of Pins |
28 |
|
Operating Voltage |
+4.0 to +5.5 V (+5.5V being absolute maximum) |
|
Number of programmable I/O pins |
24 |
|
Communication Interface |
USB Serial Interface (15,16 PINS) [Can be used for programming this controller] Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface(7,18,21,22PINS) [Can be used for programming this controller] Programmable Serial UART(17,18PINS) [Can be used for programming this controller] Two-wire Serial Interface(21,22PINS)[Can be used to connect peripheral devices like sensors and LCDs] |
|
ADC Module |
10channels, 10-bit resolution ADC |
|
Timer Module |
One8-bit counter, Three16-bit counter |
|
Analog Comparators |
2 |
|
PWM channels |
2 |
|
External Oscillator |
Up to 48MHz |
|
Internal Oscillator |
32KHz-8MHz Calibrated Internal Oscillator |
|
Program memory Type |
Flash |
|
Program memory / Flash memory |
32Kbytes[10000 write/erase cycles] |
|
CPU Speed |
12 MIPS |
|
RAM memory |
2KBytes |
|
EEPROM memory |
256Bytes |
|
Watchdog Timer |
Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chipOscillator |
|
Power Save Modes |
Available |
|
Operating Temperature |
-40°C to +85°C(+85 being absolute maximum, -40 being absolute minimum) |
Note: Complete technical details can be found in the PIC18F2550 Datasheet linked at the bottom of this page.
PIC18F2550 Replacements
PIC18F2455
PIC18F2550 Family
PIC18F4455, PIC18F4550
Brief About PIC18F2550
PIC18F2550 is one of the cheapest microcontrollers present in the market to work with and have a lot of tutorials and support available on the Internet to help beginners. The controller has 32Kbytes flash memory which is enough for many applications. Along with 24 programmable Input/output pins, it can interface many peripherals easily. With Watchdog timer to reset under error automatically the controller can be used on systems with no human interference. Having USB interface feature, you can communicate with controller from any PC without any hassle. With many features added together further promotes use of PIC18F2550 microcontroller.
How to Use PIC18F2550 Microcontroller
PIC18F2550 is used like any other microcontroller. Microcontrollers are not like digital ICs as for digital ICs all you need is to connect the power for it to work. Microcontroller needed to be programmed before getting the chip working. So for working of PIC18F2550, first we need to save the correct program file in the controller FLASH memory. Once power is provided, the controller executes this code saved in FLASH memory to create the response.
Entire process of using PIC18F2550 goes like this:
- List the functions to be executed by PIC18F2550
- Write these functions in ‘IDE software’ using a supported programming language
(MPLAB IDE for Windows OS [www.microchip.com/mplabx-ide-windows-installer ]
(For these MPLAB IDE, you can use ‘C’ language to write the application program)
- After writing the desired program compile for error elimination using IDE.
- After successful compilation IDE application generates HEX file for the written program.
- Choose the programming device (usually ‘PIC kit 3’) which establishes communication between PC and PIC18F2550.
- Run the HEX file dumping software which is related to the chosen programming device.
- Choose the appropriate program HEX file.
- Burn the HEX file (generated for written program) in PIC18F2550 flash memory using this program.
- Disconnect the programmer and connect the appropriate peripherals for the controller.
After connecting the power, the controller executes this HEX code (or machine code) saved in the memory and performers tasks as instructed.
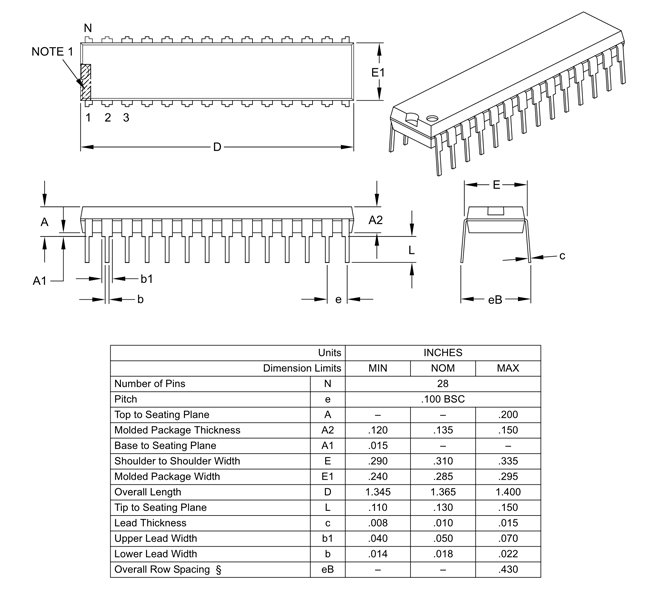
2D Model and Dimensions