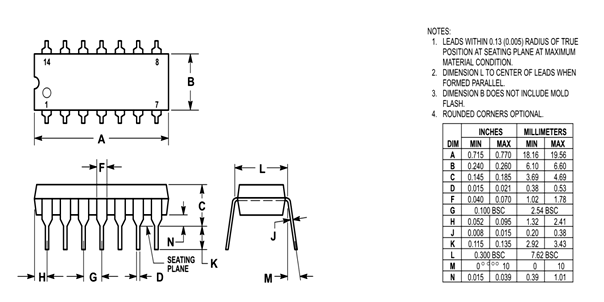
SN74LS14 Schmitt Trigger
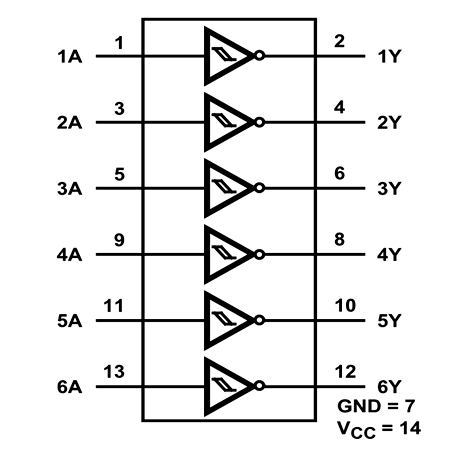
Pin Configuration
|
Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|
1,3,5,11,13,15 |
Schmitt Input Pins |
Input pins of the Schmitt trigger |
|
2,4,6,10,12,14 |
Schmitt Output Pins |
Output pins of the Schmitt trigger |
|
7 |
Ground |
Connected to the ground of the system |
|
14 |
Vcc (+5V) |
Resets all outputs as low. Must be held high for normal operation |
Features
- Schmitt Trigger – Hex Inverter
- Operating Voltage: 5V
- Low Level Hysteresis voltage: 0.25V
- High Level Hysteresis voltage: 3.4V
- Output current High: -0.4mA
- Output current Low: 8.0mA
- Hysteresis voltage: 0.8V typically
- Typical Rise Time: 12nS
- Typical Fall Time: 12nS
- Available in 14-pin PDIP, GDIP, PDSO packages
Note: Complete Technical Details can be found in the SN74LS14 datasheet given at the end of this page.
SN74LS14 Equivalents
Alternatives Schmitt Triggers
Where to use SN74LS14 IC
The SN74LS14 is a hex inverter Schmitt trigger, meaning it has 6 inverted Schmitt triggers inside it. A Schmitt trigger is used to avoid the problem of hysteresis. It can also be used to smoothen a noisy signal into sharp one. Schmitt trigger gate can convert sinusoidal or triangular wave to square wave. It can also be used as a logic inverter if needed. A Schmitt trigger is also useful for debouncing a push button or other noisy input devices.
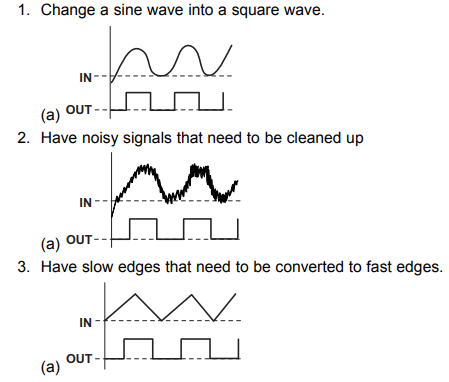
So if you are looking for an IC which can help you to get off switching noise or to create sharp square wave signals based on an input signal, then this IC could be the right choice or you.
How to Use 74LS14 IC
As mentioned earlier 74LS14 has six INVERTING SCHMITT TRIGGER GATES which can be used as six individual gates. The simplified internal structure can be given as below.
Each of these 6 gates can be used individually based on our application. Since the gates are inverting we can also combine two gates together to form a non-inverting gate. The input signal can be a noise square wave or any signal wave that oscillates between the low and high hysteresis voltage.
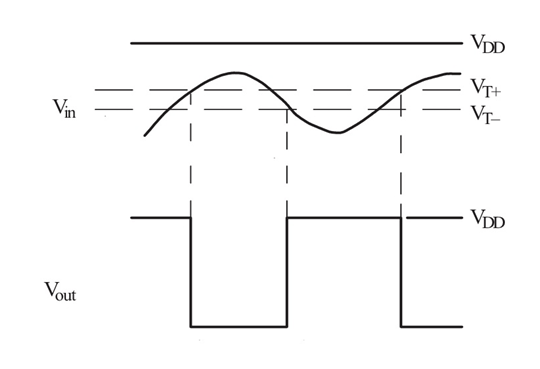
The unique and special functionality of a Schmitt trigger is to toggle the output based on the input signal without any noise. This is achieved by using a hysteresis band inside which no switching takes place. The voltage level in this band from VT+ to VT-. In our SN74LS14 IC the VT+ is 3.4V and VT- is 0.2V.
Meaning the output will get low only when the input voltage (Vin) is greater than 3.4V and will get high only when the input voltage goes below 0.2V. Any noise occurring in the input voltage between 0.2V – 3.4V will not affect the output voltage. You can use the Application report from TI to know more about using this IC
Switching Time of 74LS14 IC
The gates in 74HC14 take some time to provide output to the given input. These time delays are called switching times. Each gate will take time to turn ON and OFF. For understanding this better, let us consider the switching diagram of a gate.
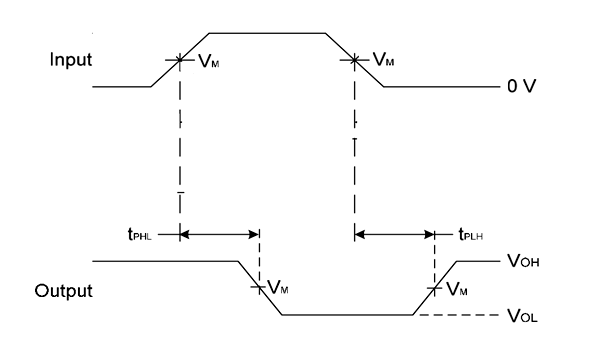
There are two delays which happen when switching. These two parameters are RISETIME (tPHL) and FALLTIME (tPLH).
In the graph, VoH goes LOW when INPUT reaches a threshold and VoH goes HIGH when INPUT goes lower than threshold voltage. In another sense it is the output voltage.
As you can see in the graph there is time delay between LOGIC INPUT going HIGH and VoH going LOW. This delay in providing response is called RISETIME (tPHL). The RISETIME (tPHL) is 12ns.
Similarly in the graph there is time delay between LOGIC INPUT going LOW and VoH going HIGH at the OUTPUT. This delay in providing response is called FALLTIME (tPLH). The FALLTIME (tPLH) is 12ns.
Total is 24ns for each cycle. These delays must be considered at higher frequencies otherwise we will have major errors due to false triggering.
Applications
- Noise removing circuits
- Debouncing circuits
- Hysteresis controller
- Dead band filter
2D Model