TE Connectivity's UAM Wi-Fi Triple Band Antennas offer a compact alternative for terminal antennas
Types of Soldering Iron Tips and How to Select the Right One?
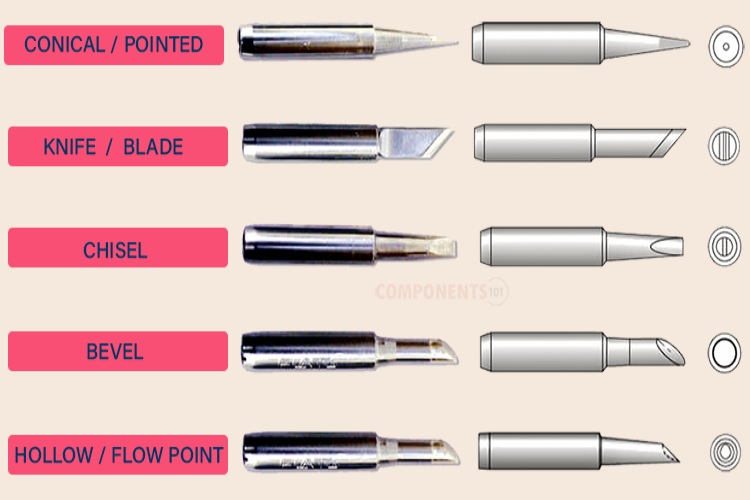
Soldering Iron Tip Basics
Soldering iron tips are crucial components of soldering irons, which are tools used for the melting and application of solder to join two metal parts together. The tip is the part of the iron that directly contacts the solder and the components being soldered, making its shape, size, and material vital for effective soldering. While soldering might be considered an easy job, people with considerable soldering experience will tell you that each ‘type’ of soldering job is different and that a single soldering iron will not suffice for every job. More specifically, the type of soldering iron tip used for the job determines how easy a particular soldering job is, and to a lesser extent, the quality of the final product.
Why Do You Need Different Types of Tips?
Different soldering tasks require different types of tips, as the shape and size of the tip can significantly affect heat transfer, precision, and accessibility. For example, soldering a large joint requires a tip that can transfer more heat to a bigger surface area, while delicate soldering on a circuit board requires a smaller tip for precision and to avoid damaging nearby components.
The most important thing to keep in mind is that the type of tip directly determines the amount of heat transferred to a joint, and care must be taken to ensure that the right tip is used for the right application to prevent damaging sensitive components and at the same time transferring enough heat to complete large joints.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of soldering tips to give you an idea of which one might be the right choice for you. Again, make sure to select the tip also based on the soldering iron you have, if you are not sure what type of soldering iron you have or how to choose one, consider reading our article on 'Types of Soldering Iron and How to Select the Right One'.
Most Commonly Used Soldering Tips
There are several types of soldering iron tips, but the most commonly used include:
1. Conical Soldering Tip
Conical tips, also known as pointed tips, are shaped like a cone and come to a sharp point. They are particularly useful for precision work where high accuracy is required. This type of tip is ideal for soldering at intricate joints or in dense circuit board areas where other tips might damage neighboring components. Due to their shape, conical tips are excellent for reaching difficult spots but are not the best for heat retention, making them less suitable for soldering larger components.
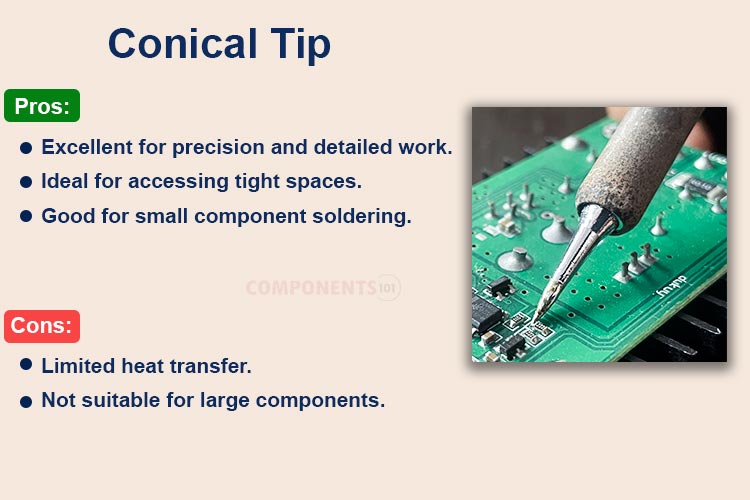
They are good for beginners and for fine work such as SMD soldering. Tips with different ‘sharpnesses’ are available for different jobs, with fine tips being available for SMD soldering and larger tips being used for things like connecting wires to pads.
Uses and Advantages of Conical Soldering Tip:
- Precision electronics soldering
- Working with SMD components
- Detailed work in confined spaces
2. Beveled Soldering Tip
Bevel tips, sometimes referred to as hoof tips, have a flat surface with an angled edge, resembling a hoof. The surface is normally angled at 45 degrees. This design allows for a larger surface area to come into contact with the solder joint, making bevel tips suitable for both precision and general soldering tasks. They are particularly effective for drag soldering, a technique used in soldering multiple pins in a row, like those on ICs Bevel tips provide a good balance between precision and heat transfer efficiency.

This feature makes them more versatile compared to conical tips, the fine end makes them useful for fine work like SMD soldering, and the flat ends can be used to transfer a lot of heat to more challenging joints. It is because of their versatility that they are recommended for everyday use.
Uses and advantages of Beveled Soldering Tip:
- Soldering at an angle
- Situations requiring both precision and heat capacity
- Working with both small and medium-sized components
3. Chisel Soldering Tip
Chisel tips are flat and wide, resembling a chisel. They offer a large surface area, making them ideal for soldering larger components and joints where substantial heat transfer is required. Chisel tips are commonly used in applications where the soldering points are not exceptionally small, such as in through-hole PCB soldering and larger wire splicing. Their shape allows for quick and efficient heat delivery, making them suitable for both beginner and professional use.

Since they have a large surface area compared to other kinds of tips, they are well suited to soldering wires to large pads or tinning a large ground plane which requires a lot of heat transfer. This kind of tip also helps with desoldering because of the large surface area.
Uses and Advantages Chisel Soldering Tip:
- General electronics work
- Soldering wires and terminals
- Applications requiring quick heat transfer
4. Knife Soldering Tip
Knife tips, as the name suggests, have a shape similar to a knife blade. Due to their shape, they are also called blade tips. This design is especially useful for soldering in tight spaces where a flat tip is needed but a chisel tip is too large. They are also excellent for drag soldering, particularly in cases.

Where the soldering points are aligned in a row but not perfectly straight, such as in SMD (Surface Mount Device) components. Knife tips can also be used for cutting away excess solder or for solder bridging.
Uses and Advantages of Knife Tip:
- Drag soldering SMD components.
- Soldering in grooves or slots
- Working on areas requiring a broad yet precise tip
5. Flow or Hollow Point Soldering Tip
Flow or hollow point tips have the same shape as a bevel tip, with a concave hollow or a tunnel at the end of the tip. This unique design is beneficial for situations where the solder needs to be precisely directed and controlled. The hollow point can hold a small amount of solder, allowing for consistent and controlled flow onto the joint.
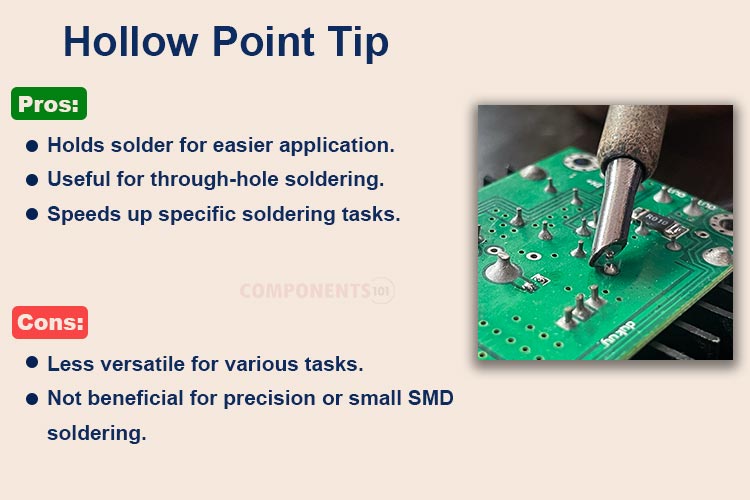
These tips are particularly useful for tasks requiring a high degree of precision and minimal solder waste, such as in delicate electronic work.
Uses and Advantages of Hollow Soldering Tip:
- Automated soldering processes
- Situations requiring consistent solder application.
- Jobs requiring a larger amount of solder.
6. Bent Soldering Tip
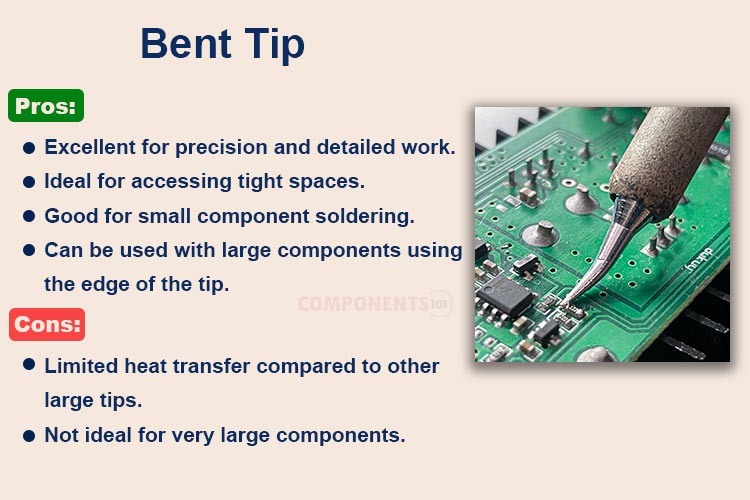
These are normal conical tips with a bend at the end. This type of tip finds use in niche applications for hard-to-reach joints. They can be found normally used by repair technicians and are available in different sizes just like a conical tip.
Soldering Iron Tip Material
The material of a soldering iron tip affects its durability, heat transfer capability, and wetting properties. Copper is a common base material due to its excellent thermal conductivity, often plated with iron to resist erosion and solder corrosion. Some tips are further plated with nickel and chromium to prevent solder from adhering to the tip, extending its life and performance.
Commonly Asked Questions
● How often should I replace my soldering iron tip?
The lifespan of a soldering iron tip depends on several factors, including the quality of the tip, how often it's used, and how well it's maintained. Generally, a tip can last from a few months to a few years. Signs that you need to replace your tip include noticeable wear, inability to hold solder, or difficulty transferring heat effectively.
● Can I use one soldering tip for all my soldering needs?
While a versatile tip like a chisel tip can be used for a variety of soldering tasks, using the right tip for the job is crucial for optimal results. Different tips are designed for specific purposes, such as precision work or soldering large joints. Having a selection of tips and choosing the appropriate one for each task will improve your soldering quality and efficiency.
● How do I clean my soldering tip?
Proper cleaning involves wiping the tip on a damp sponge or brass tip cleaner to remove oxidation and excess solder. This should be done both during and after soldering sessions to maintain tip health. Additionally, applying a thin layer of solder to the tip after cleaning (tinning) can help protect it from oxidation.
● Why does my soldering tip turn black and not take solder?
This is usually due to oxidation, which prevents the solder from wetting the tip. Keeping the tip clean and properly tinned during use can prevent this issue. If the tip is already oxidized, you may need to use a tip tinner or a tip activator to restore its surface.
● What temperature should I set my soldering iron to for different tips?
The optimal temperature depends on the soldering task, the type of solder you're using, and the tip's material. Generally, temperatures between 300°C (572°F) and 370°C (698°F) are suitable for most tasks. However, delicate components may require lower temperatures, while larger joints that need more heat might require temperatures at the higher end of this range. It's essential to adjust the temperature based on the specific requirements of your project and the manufacturer's recommendations for the tip.
● What is the best Soldering Tip for SMD?
For soldering Surface-Mount Devices (SMD), bevel or hoof tips are often recommended. Their shape allows for a good transfer of heat to small pads without damaging adjacent components. Knife tips can also be useful for drag soldering multiple pins in a row.
● What is a T12 Soldering Tip?
T12 soldering tips are a specific type of soldering iron tip designed for use with certain soldering stations made by Hakko. These tips are known for their quick thermal recovery and high thermal conductivity, making them ideal for jobs requiring consistent heat. The T12 tip has the heating element and the thermocouple built into it just like the JBC C245 and C210 tips,, making it much more efficient and stable than normal soldering iron tips. T12 tips come in various shapes, including those mentioned above, allowing for versatility in soldering tasks.
● What Are Different Soldering Iron Tips Used For?
Different soldering iron tips are designed for specific tasks: ○ Conical and Bevel Tips: Ideal for precision work on electronic components. ○ Chisel Tips: Best for general soldering, including wires and larger components. ○ Knife Tips: Useful for soldering in tight spaces and for specific techniques like drag soldering. ○ Flow or Hollow Point Tips: Excellent for through-hole soldering, where solder needs to be applied generously.
Conclusion
Selecting the right soldering iron tip is crucial for achieving the best results in any soldering project. Conical tips are best for precision work, bevel tips for a mix of precision and heat, chisel tips for general soldering, knife tips for drag soldering, and flow or hollow point tips for consistent solder application. Understanding the strengths and applications of each tip type can greatly enhance the efficiency and quality of your soldering work, whether you're a professional or a hobbyist. Even though these are the facts, each user's personal preferences also have a huge role. For example, I would like to use smaller bevel tips for most of the use cases, from 0201 SMD parts to through-hole parts.








