2N4401 NPN Transistor
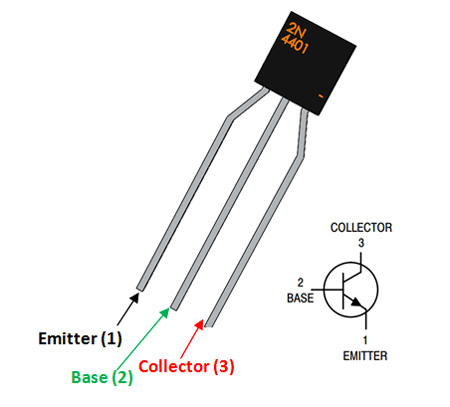
2N4401 Pin Configuration
|
Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|
1 |
Emitter |
Current Drains out through emitter, normally connected to ground |
|
2 |
Base |
Controls the biasing of transistor, Used to turn ON or OFF the transistor |
|
3 |
Collector |
Current flows in through collector, normally connected to load |
Features
- General purpose NPN Transistor
- High DC Current Gain (hFE), typically 80 when IC=10mA
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 500mA
- Collector-Emitter voltage (VCE) is 40 V
- Collector-Base voltage (VCB) is 60V
- Emitter Base Breakdown Voltage (VBE) is 6V
- Transition Frequency is 100MHz
- Available in To-92 Package
Note: Complete technical details can be found in the 2N4401 datasheet attached at the bottom of the page.
Alternative NPN Transistors
BC549, BC636, BC639, BC547, 2N2369, 2N3055, 2N3904, 2N3906, 2SC5200, 2N5551
2N4401 Equivalent Transistors
2N3904, 2N2222A
Brief Description on 2N4401 Transistor
2N4401 is a NPN transistor hence the collector and emitter will be left open (Reverse biased) when the base pin is held at ground and will be closed (Forward biased) when a signal is provided to base pin. 2N4401 has a gain value hfe of 500; this value determines the amplification capacity of the transistor. The maximum amount of current that could flow through the Collector pin is 800mA, hence we cannot connect loads that consume more than 500mA using this transistor. To bias a transistor we have to supply current to base pin, this current (IB) should be limited to 5mA.
When this transistor is fully biased then it can allow a maximum of 800mA to flow across the collector and emitter. This stage is called Saturation Region and the typical voltage allowed across the Collector-Emitter (VCE) or Base-Emitter (VBE) could be 200 and 900 mV respectively. When base current is removed the transistor becomes fully off, this stage is called as the Cut-off Region and the Base Emitter voltage could be around 660 mV.
Where 2N4401 Transistor is Used
The 2N4401 transistor is very much similar to the commonly used NPN transistor 2N2222. But there are two important features that differentiate the 2N4401 and 2N2222. 2N4401 can allow collector current upto 500mA only and also has power dissipation of 652mW which can be used to medium loads than compared with 2N2222, but can drive loads more than BC547.
So if you are looking for an NPN transistor that could switch loads or for decent amplification, then 2N4401 might the right choice for your project.
How to use 2N4401 Transistor
This transistor like all can be used either as a switch or as an amplifier. The Base-Emitter voltage of this transistor is 6V so you just have to supply this voltage across the base and emitter of the transistor to induce a base current into the transistor. This transistor will make it forward biased and thus closes the connection between collector and emitter. However one important thing to notice is the Base resistor a.k.a current limiting resistor. As the name suggests this resistor will limit the current flowing through the transistor to prevent it from damaging. The value for this resistor can be calculated using the formula
RB = VBE / IB
To make things simple I have shown a simplified circuit to make a transistor as switch. In actual circuit modifications might be required. I have used a base voltage of 5V and a value of 1K as current limiting resistor
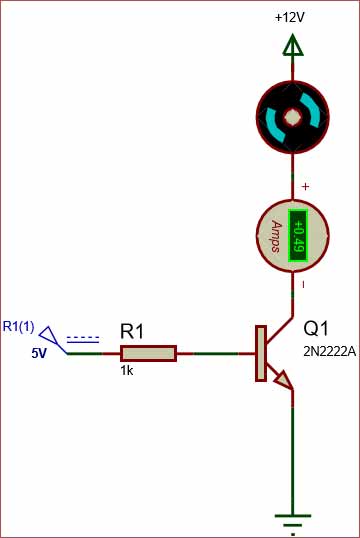
Note that the motor here draws about 500mA from the 12V power source, since the 2N4401 has collector current rating upto 500mA this circuit is possible had it been a BC547 the transistor should have been burnt.
Applications
- Can be used to switch high current (upto 500mA) loads
- It can also be used in the various switching applications.
- Speed control of Motors
- Inverter and other rectifier circuits
- Can be used in Darlington Pair.
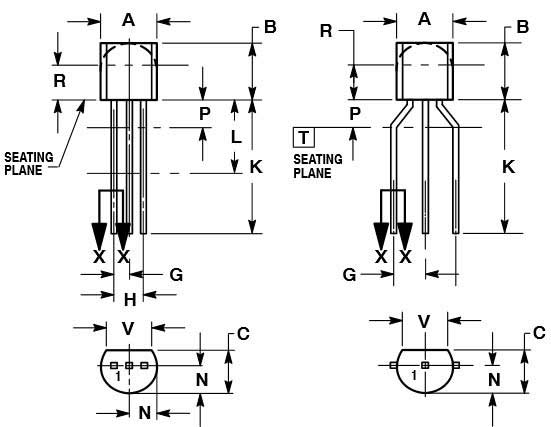
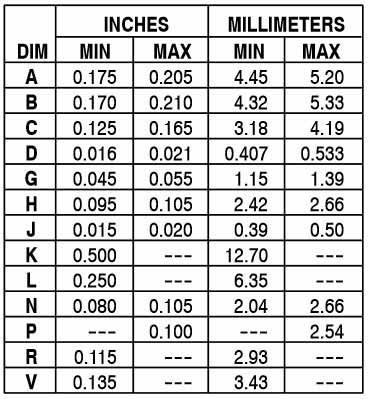
2D-Model and Dimensions
2D dimensions will help you in placing this component at the time of making circuit on perf board or a PCB.