AHV85003 and AHV85043 isolated SiC gate driver chipsets are optimized for driving discrete SiC FETs
Different Types of Proximity Sensors with Working & Applications
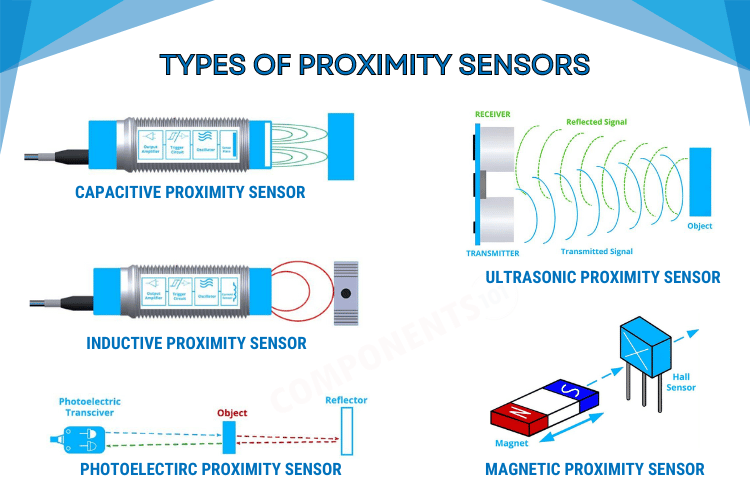
Proximity sensors play a crucial role in modern industries, enabling automation, safety, and efficiency in various applications. These sensors are designed to detect the presence or absence of objects within a certain range without physical contact. In this article, we will delve into the different types of proximity sensors commonly used in industries, understanding their working principles and exploring their applications.
This article covers only Proximity Sensors, If you wanna know more about sensors in general, you can check out different kind of sensors articles by following the link.
Inductive Proximity Sensors
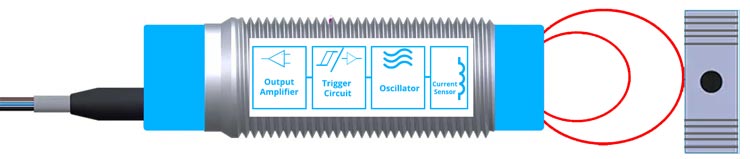
Inductive proximity sensors are widely used in industrial environments for their robustness and reliability. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an object approaches the sensor's electromagnetic field, it induces eddy currents, leading to a change in the sensor's output.
Applications of Inductive Proximity Sensors
Inductive proximity switches are effective in detecting metal objects and are commonly employed in position sensing, object detection, collision detection, speed sensing and automated machinery. They are also used in industrial manufacturing facilities to detect the presence of metallic objects.
Examples of Inductive Proximity Sensors
If we look at Inductive proximity sensors the most popular ones are the LJ12A3-4-Z/BX, PR12-DN, and SN04-N.
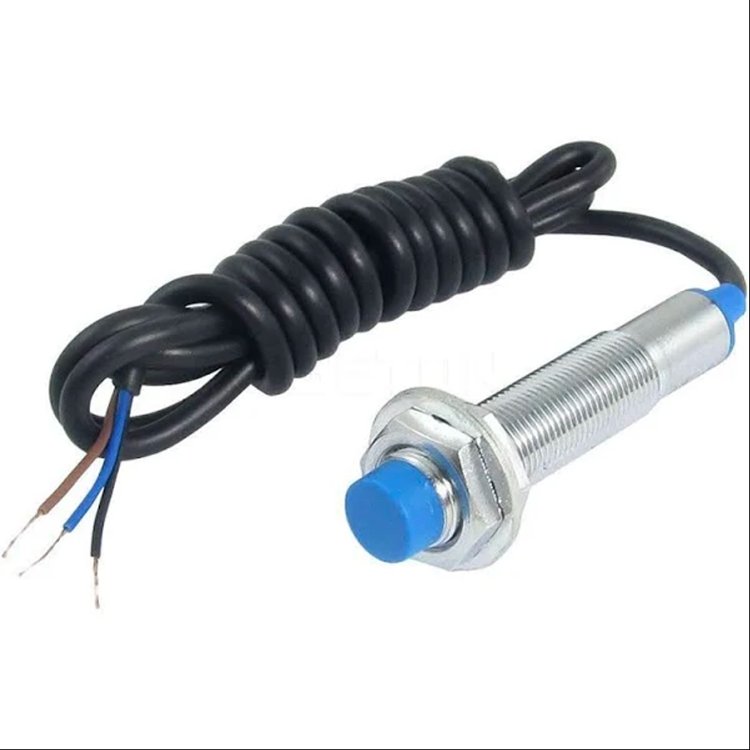

Capacitive Proximity Sensors
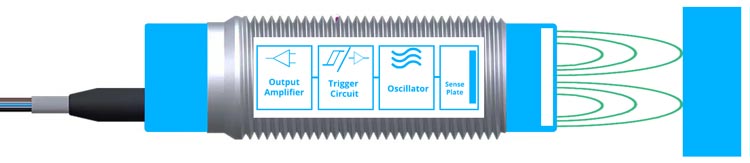
Capacitive proximity sensors are versatile and can detect a wide range of materials, including conductive and non-conductive substances. These sensors consist of two plates separated by a dielectric material. When an object enters the sensor's electrical field, it alters the capacitance between the plates, triggering a change in the output signal.
Applications of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
Capacitive proximity switches are commonly used in applications such as level sensing, liquid detection, and object proximity detection in harsh environments. they are widely used in automatic pump control systems to detect water levels.
Examples of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
The most popular capacitive proximity sensors in the market are CR18-8DN, CR30-15AO, M12, M18, and M30.
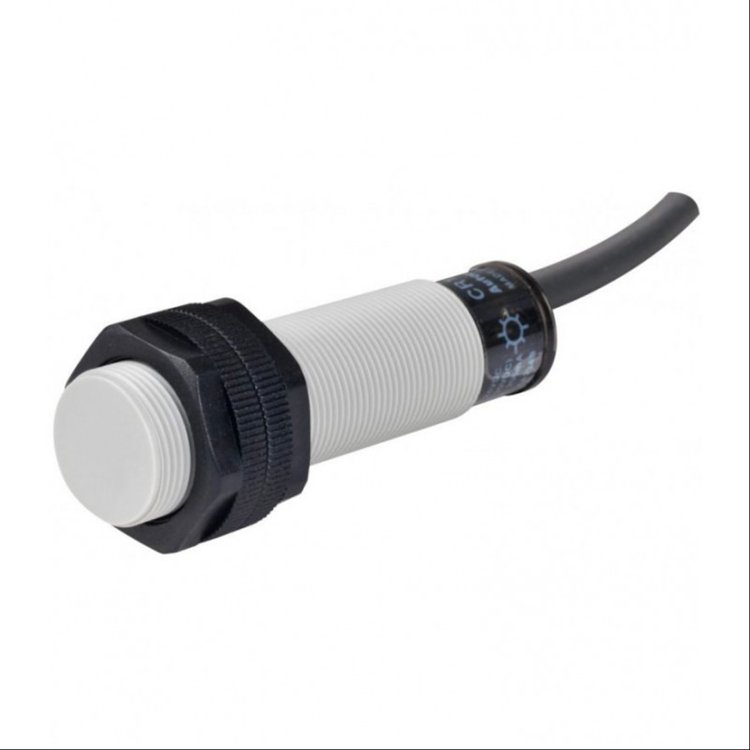

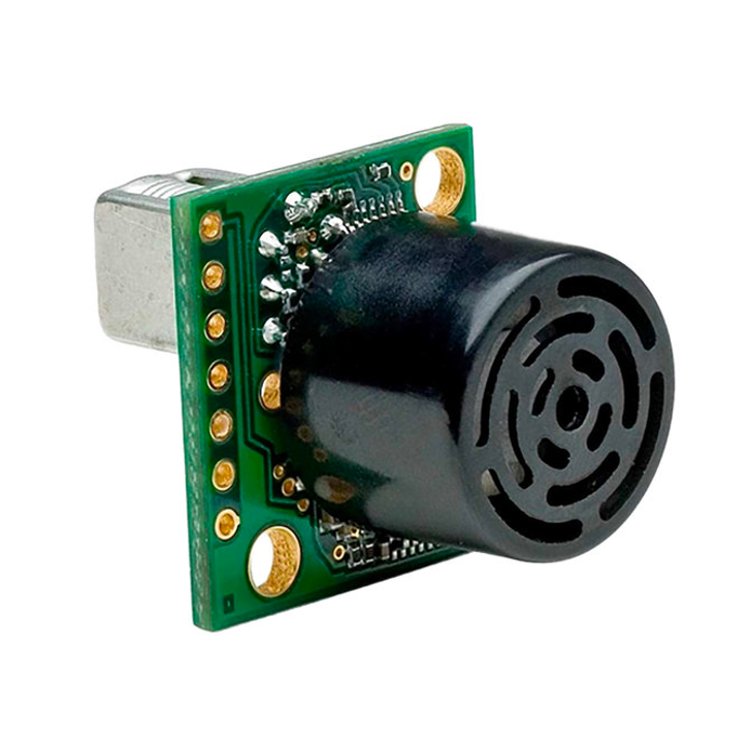
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
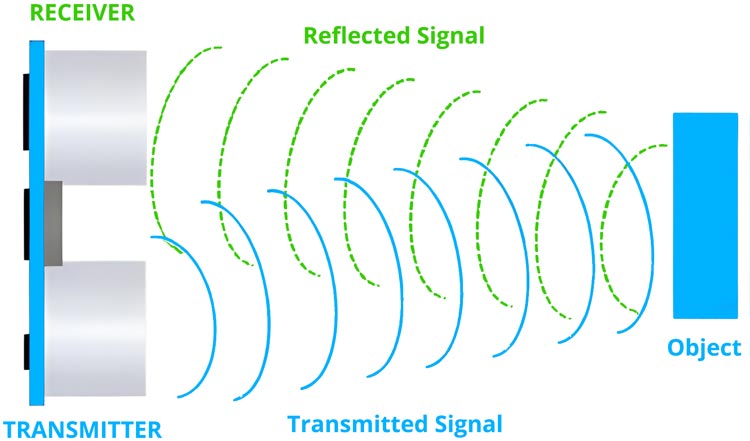
Ultrasonic proximity sensors utilize sound waves to detect objects. These sensors emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back after hitting an object. By analysing the time delay, the sensor determines the distance to the object.
Applications of Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors are effective in detecting a wide range of materials and are commonly used in presence detection, level sensing, and collision avoidance systems. They are also used in autonomous vehicles for object detection.
Examples of Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
Some of the popular Ultrasonic proximity sensors include MB1242, MB1001, NU40A14T-1 and MB1634HRLV.

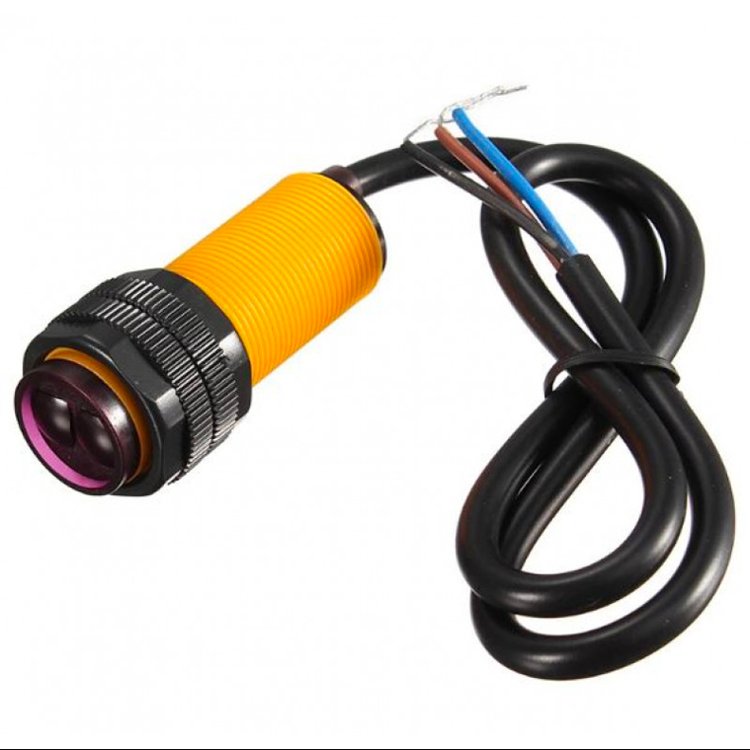
Photoelectric Proximity Sensors
Photoelectric proximity sensors employ light to detect the presence or absence of objects. They consist of a light emitter and a receiver. When an object interrupts the light beam, it causes a change in the receiver's output. Photoelectric sensors are available in various types such as through-beam, retro-reflective, and diffuse reflective. They are widely used in conveyor systems, packaging, and object-counting applications. Depending on the sensing method, there are the main types of photoelectric proximity sensors.
Through beam method
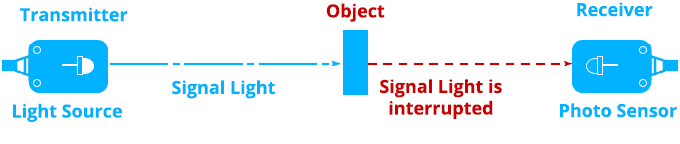
In this kind of technique, an emitter delivers a beam of light directly toward a receiver in its line of sight. This laser beam identifies the presence when an object breaks it. This kind of system necessitates the use of both an emitter and a separate detector, which makes the installation and wiring process more difficult. The advantage is that it has the largest sensing range and is the most accurate of the sensing techniques.
Retro-reflective method
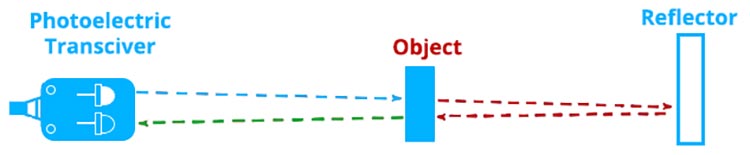
This approach detects when the light path is disturbed or broken. The housing contains both the light-emitting and light-receiving components. The reflector receives light from the emitting element, which bounces it back to the receiving element. The light is interrupted when a target is present. One benefit of employing a retro-reflective sensor over a through-beam sensor is the convenience of only needing to put a reflector on the opposite side.
Diffuse or Reflective method
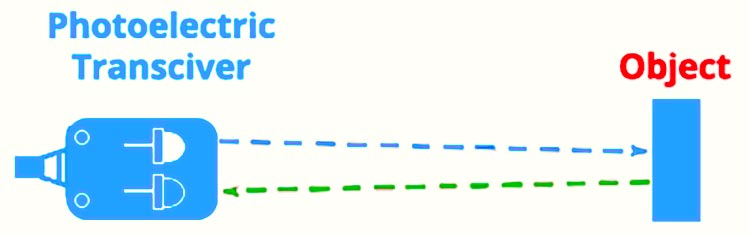
In this type of sensor emitter and receiver circuits are housed together, similar to retroreflective sensors. The light reflected by the target is picked up by the sensor. Instead of using a reflector to bounce the light back to the detector, the object itself acts as the reflector, returning some of the light to the detector to detect and register an object's presence. The diffuse sensors are primarily used in public restroom sinks, where they operate automatic faucets. Diffuse or reflective sensors are somewhat colour dependent, certain versions are suitable for distinguishing dark and light targets in applications that require sorting or quality control by contrast.
Applications of Optical Proximity Sensors
The optical type proximity sensors are widely used in conveyor systems, packaging, automatic dispensers, and object-counting applications. You can easily find such sensors in everyday objects like automatic soap dispensers, toys, vending machines, automatic doors etc.
Examples of Photoelectric Proximity Sensors
Some of the popular Photoelectric proximity sensors includes E18-D8NK, TCRT5000, and RPR220.

Magnetic Proximity Sensors
Magnetic proximity sensors rely on the detection of changes in the magnetic field to identify the presence of objects. They consist of a magnet and a reed switch or Hall-effect sensor. When a ferrous object approaches the sensor, it alters the magnetic field, causing the switch or sensor to detect the change. Magnetic sensors are commonly used in speed sensing, door position detection, and security systems. There are various technologies used in magnetic proximity sensors:
-
Reed switches
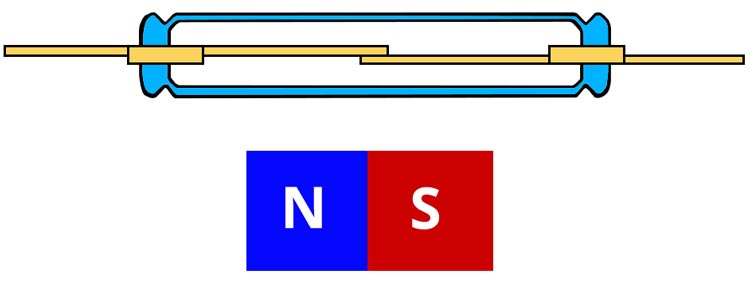
Reed switch-based magnetic sensors are made up of a glass bulb that is hermetically sealed. Two magnetic 'reeds' are enclosed in the glass bulb. The two reeds make contact with one another when a magnet is positioned close to the switch, completing the circuit.
- Hall effect Sensors
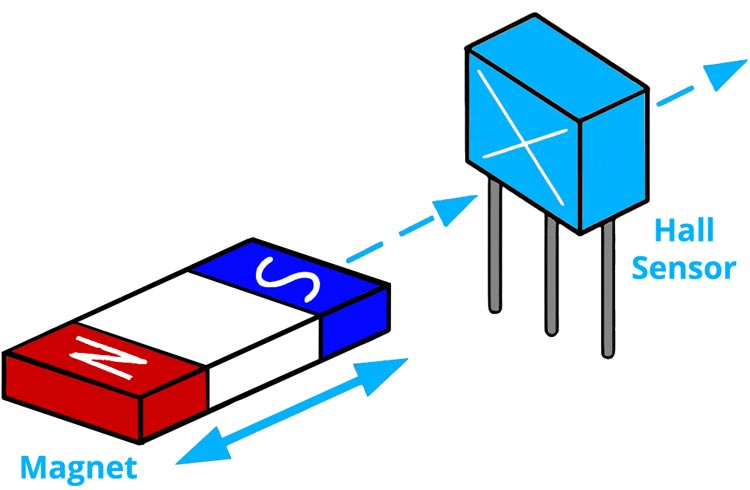
Hall effect sensors use the principle of the same name to measure the magnetic field generated by a magnetic object. There are two types of Hall sensors, digital and analog. Digital sensors output a logic HIGH or LOW signal. Analog sensors output a voltage/current proportional to the strength of the magnetic field.
-
GMR (Giant Magneto-Resistive Effect) Inductive
A Wheatstone bridge circuit is the main component of GMR sensors. Two of the resistors are specifically made using ferromagnetic and non-ferromagnetic materials used inside. Consequently, the resistance of the resistors changes when they are exposed to a magnetic field.
Applications of Magnetic Proximity Sensors
Magnetic sensors are commonly used in speed sensing, door position detection, and security systems. They can be found in burglar alarms, cooling fans, electric vehicles, etc
Examples of Inductive Proximity Sensors
Popular magnetic proximity sensors are the SEN-K11010, MC-38, PR-3150 and NJK-5002.
Comparison of Proximity Sensors
|
Proximity Sensor Types |
Inductive Proximity Sensor |
Capacitive Proximity Sensor |
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensor |
Optical Proximity Sensor |
Magnetic Proximity Sensor |
|
Operation Principle |
Based on current induced by magnetic fields to detect nearby metal objects |
Based on that when an object bets near the sensor, it changes the. capacitance between the sensing elements. |
Based on ultrasonic waves and time taken to reflect it back. |
It consists of a light sensor, which will be triggered by an object. |
Based on magnetic field. When a magnet is near the reed switch will be activated. |
|
Material supported |
Metallic only |
All material |
All material |
All material |
Magnet |
|
Operating distance |
<50mm |
<50mm |
15m |
100mm |
<80mm |
|
Cost |
Low |
Moderate |
High |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Environmental factors affecting Sensitivity |
Metal Objects |
Humidity& vapors |
Air flow & temperature variation |
Dust, oil, aspect of object |
Magnets, EMI, Metals |
Are Proximity Sensors and Distance Sensors the same?
Distance sensors are used to measure distance from an object by measuring distance. Proximity sensors, on the other hand, are used to detect objects in a particular range without specifying how far away they are. Most of them will only give a trigger output when an object is detected. But distance sensors can be used as proximity sensors with the help of a microcontroller








