2N4402 General Purpose PNP Transistor
The 2N4402 is a PNP silicon transistor designed for general purpose amplifier and switching applications. This transistor comes with a VCE of 40V and a continuous collector current of 600mA. It can be used as a small signal switching transistor. It also has a low base voltage of 5V.
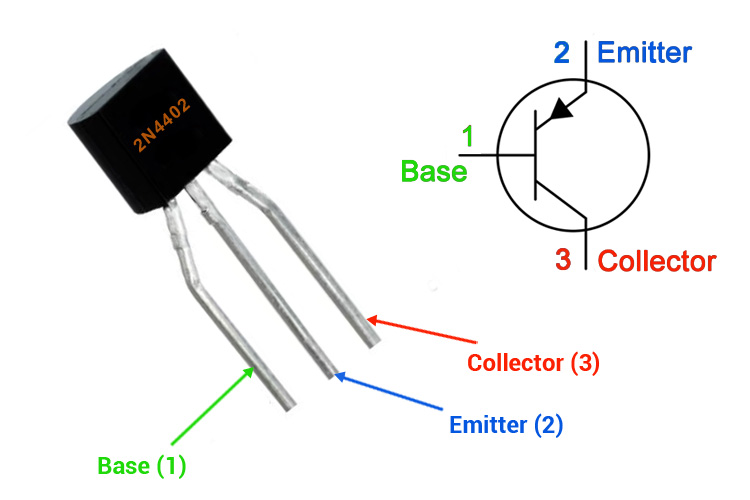
2N4402 Pinout Configuration
|
Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|
1 |
Base |
Controls the biasing of the transistor |
|
2 |
Emitter |
Electrons emitted from the emitter into the first PN junction |
|
3 |
Collector |
Electrons Emitted from Emitter Collected by the Collector |
Features & Specifications
- Bi-Polar NPN Transistor
- DC Current Gain (hFE) is 150 maximum
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 600mA
- Emitter Base Voltage (VBE) is 5V
- Base Current (IB) is 50mA maximum
- Available in TO-92 Package
- Maximum Collector-Base Voltage |Vcb|: 45 V
- Collector Dissipation: 0.3 W
- Transition Frequency:100 MHz
- Operating Junction Temperature Max (Tj): 175 °C
- Noise Figure: 2-10 dB
- Operating and Storage Junction Temperature Range -55 to +150 °C
- Collector Capacitance 8.5 pF
- Pb−free packages are available
Note: Complete Technical Details can be found in the 2N4402 Transistor datasheet given at the end of this page.
2N4402 Equivalent Transistor
BC559, BC327, BC556, NTE159, 2N4403
Basic Working of a Transistor
The 2N4402 Transistor is a general-purpose P-N-P transistor, A junction transistor is a sandwiched construction between two layers of N-type material or P-type material, depending upon the construction transistors are divided into two categories NPN transistor and PNP transistor, which are shown below, transistors are made up of silicon or germanium, depending upon the application it is chosen.
General Description of 2N4402 Transistor
2N4402 is basically used when you want a simple switching device for low power loads. The component is cheap and easy to work with so it is best suited when choosing a random switching device. 2N4402 can also be used as a basic power amplifier and its application includes amplifying low power signals.
When this transistor is in a biased condition, then it can allow a maximum current of 600mA across CE(Collector-Emitter) Junction, this state of the transistor is called the saturation state, and driving a load that consumes more current than 600mA may damage the device in this condition. As you already may know a transistor is a current-controlled device so when the base current is removed the transistor becomes fully off, in this stage the transistor is working in its Cut-off Region and no current flows through the C-E junction. The 2n4402 transistor has a gain of 20 to 150 this value determines the amplification capacity of the transistor, the peak current that can be flown through this transistor is 200maA, which combines with the gain value makes this transistor a perfect choice for a preamplifier for audio amplifier.
Under normal circumstances and without external influence there will be a positive voltage appearing at the base of the PNP transistor. As we all know, based on the working principle of a PNP transistor; having a positive voltage at the base puts a PNP transistor in a high resistance state. By characteristic a small amount of current needs to flow out of the base of the transistor to completely turn on the device, for this device you can see to flow 500mA of current through the collector to emitter, 50mA of current needed to flow through the base of the transistor.
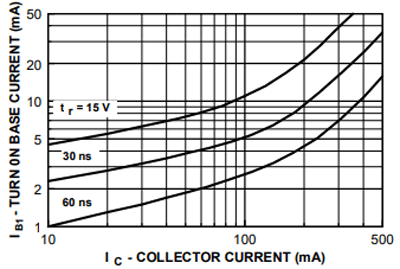
How to use 2N4402 Transistor
Transistors are current-controlled devices so to turn them on a little current is needed. For the 2N4402 Transistor, this base current is less than 50mA, as 2N4402 is a PNP transistor that means it will be on when the base is connected to the ground, and it will be off when a positive voltage is applied to the base of the transistor.
The simulated circuit below shows how this transistor behaves when the base of the basic circuit is connected to the ground and when it's connected to 5V of the power supply.
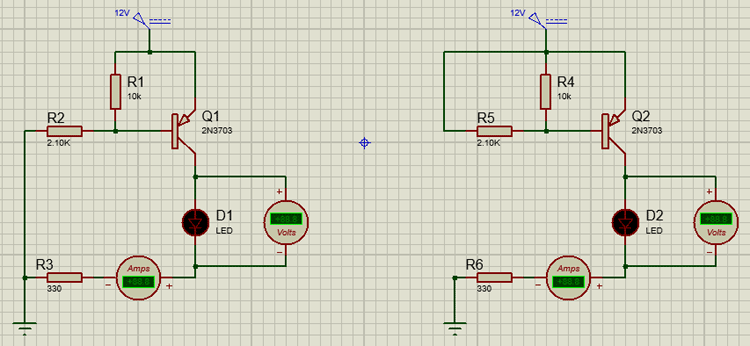
When we turn on the transistor by connecting the base to the ground the transistor will remain on unless the voltage at the base of the transistor reaches more than the base turn-off voltage, for this transistor, it is somewhere in between 0.7 -0.9V. The base of the transistor cannot be left floating otherwise there could be false triggering, which may lead to issues in the circuit. To resolve the issue we need to add pullup resistors as shown in the example a 10K resistor is used to pull up the base of the transistor to VCC.
Applications
- Simple switching applications
- Microphone preamplifiers
- Lighting systems
- Relay drivers
- Audio Amplifiers
- Signal Amplifiers
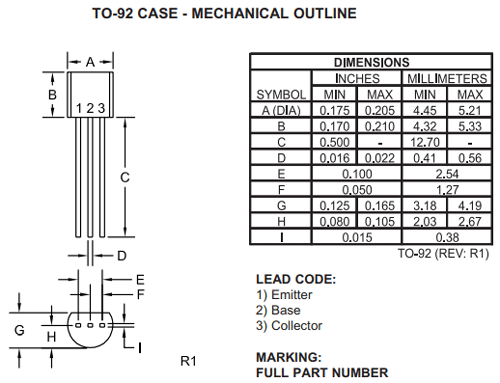
2D Model and Dimensions
If you are designing a PCB or Perf board with this component then the following picture from the 2N4402 Datasheet will be useful to know its package type and dimensions.