BSS84 P-Channel MOSFET
BSS84 is P-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) and is used as a high speed switching device in applications. The device is designed using ON Semiconductor’s proprietary, high cell density, DMOS technology. This very high density process minimizes on-state resistance and to provide rugged and reliable performance and fast switching.
Pin Configuration
BSS84 is a three pin device as shown in figure and the function of each of those pins is stated below.
|
Pin |
Name |
Function |
|
1 |
Drain |
Current which comes in to the device through Source pin goes out through Drain pin. |
|
2 |
Gate |
MOSFET gets turned ON and OFF depending on voltage applied at this pin. |
|
3 |
Source |
Current comes in to the device from Source pin. |
BSS84 Features and Specifications
- P-Channel MOSFET
- Enhancement mode MOSFET
- Low threshold voltage
- High-speed switching
- Very low turn ON resistance
- No secondary breakdown
- Direct interface to CMOS and Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL)
- Maximum Drain-Source voltage: -50V
- Maximum Gate-Source voltage: ±20V
- Maximum continuous Drain current: -130mA
- Pulsated Drain current allowed: -1.2A
- Maximum power dissipation: 0.30W
- Operating temperature range: -55ºC to +150ºC
Similar MOSFETs
TSM2309, ZXMP2120FF, NDS332P, IRLML6402, AO3401
BSS84 MOSFET Overview
- BSS84 can be used as high speed switching device replacing all conventional transistors in digital circuits since it is specifically designed with high cell density process for high speed switching applications.
- BSS84 is specifically designed to be used in low voltage applications and hence the device is preferred in battery operated systems.
- The device is manufactured using special design process leading to very low turn ON resistance during operation. This low turn ON resistance characteristic is a must condition in some applications.
- As the low drop during operation leads to less power loss efficiency of the system will be more if the device is used. Hence the device is can also be used in high efficiency applications.
How to use BSS84 MOSFET
For understanding the working of BSS84 let us consider a simple application circuit as shown below.
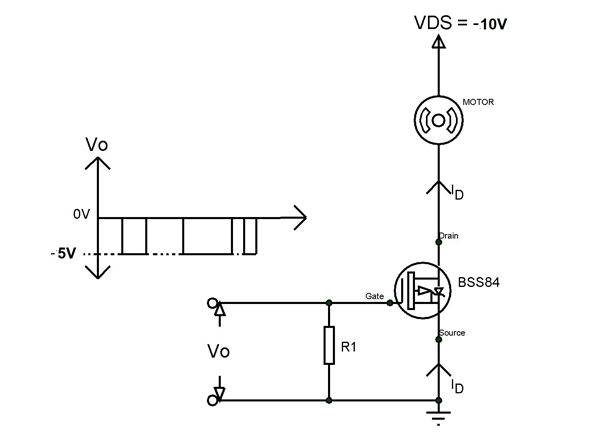
Here BSS84is used as a simple switching device while small motor acts a load. The trigger for the gate of the MOSFET is provided from a voltage signal Vo which is output from a microcontroller or microprocessor. The MOSFET is powered from a negative power source of VDS = -10V as shown in figure.
Now let us remember the characteristics of P-channel enhancement MOSFET:
- The MOSFET does not conduct when the voltage at the Gate-Source junction does not go below a certain threshold voltage.
- The current flow through Drain is determined by the voltage at the gate terminal up to a certain point. So lower the gate voltage, lower the MOSFET conduction resistance and higher the drain current.
- The p-channel MOSFET conducts only when a negative voltage present at the gate terminal, so the instant the gate voltage removed the MOSFET stops conducting.
We will apply the same characteristics in above circuit for understand the working.
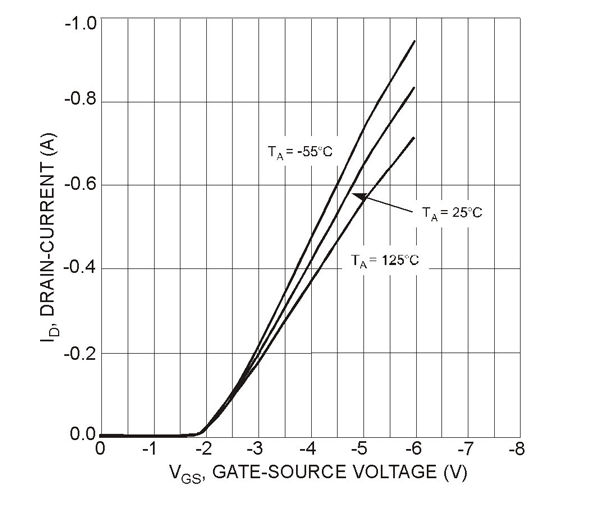
Now consider the Vo is not provided to the gate of the device: under such case the MOSFET will not conduct as based on characteristic graph as shown below a minimum negative voltage of -2V need to be present at the gate for switching ON the device.
Under presence of Vo: When the gate pulse of -5V is provided by the microcontroller at a certain time as shown in circuit diagram the MOSFET will start conduction. So now current ID flows through the device and this current flow leads to a voltage drop across motor and this drop will turn ON motor. This motor will continue to rotate until the negative voltage from the controller is present and the instant the Vo goes to 0V the motor stops rotating.
Hence by using the above circuit we have used BSS84 as a switching device and in a similar way we can use the device in other application circuits.
Applications
- Line current interrupter in telephone sets
- Relay, high-speed and line transformer drivers
- Battery operated systems
- Power management functions
- Basic switching applications
- Simple switching applications
- Lighting systems
- Signal Amplifiers
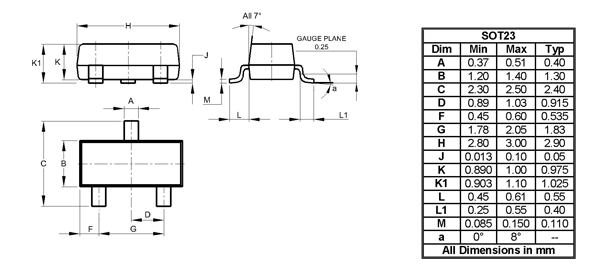
2D-Model