AHV85003 and AHV85043 isolated SiC gate driver chipsets are optimized for driving discrete SiC FETs
Understanding Constant Current and Constant Voltage Sources
Constant current (CC) sources and constant voltage (CV) sources are the two types of power sources to take into account while working with electronics. These terms describe how a power source supplies energy to a load, but they serve distinct purposes in different applications. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals, characteristics, and common use cases of both constant current and constant voltage sources.
What is a Constant Voltage Source?
A constant voltage (CV) source is a type of power supply designed to maintain a steady output voltage regardless of variations in the load current. The main goal of a CV source is to keep the voltage constant, even if the load changes or fluctuates. Ie. even if there is no load or if the load is at maximum the power supply will keep the output voltage at a constant level. Keep in mind that if the load current is more than that of the ratted maximum the output voltage can collapse. Byt sources with over current protection this won't be an issue. Such supplies will automatically turn off when the ΔV exceeds the limit.
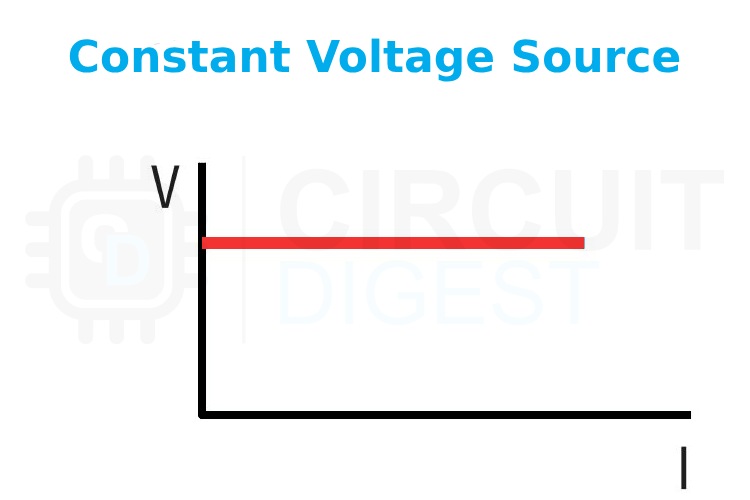
The above image shows the typical graph plotting the output voltage of a constant voltage source. As you can see the output voltage remains constant, even with increasing current.
Characteristics of Constant Voltage Source:
- Fixed Output Voltage: The primary feature of a CV source is its ability to supply a consistent voltage output regardless of the load current.
- Varying Current: The output current changes depending on the load. As the resistance or impedance of the load changes, the current drawn by the load will adjust to maintain the same voltage.
- Applications: Constant voltage sources are widely used in devices that require a stable voltage supply, such as:
- Powering digital electronics (e.g., microcontrollers, sensors, processors).
- Battery chargers (in CV mode, after the initial constant current phase).
- General-purpose power supplies for testing and development.
Example: A typical USB charger operates as a constant voltage source. For example, a 5V USB charger will always try to deliver 5V to the connected device, but the current drawn will depend on the power needs of the device being charged.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Easy to use for most electronics, stable voltage ensures reliable operation of devices.
- Cons: Not suitable for applications where a fixed current is required, such as LED drivers.
What is a Constant Current Source?
A constant current (CC) source supplies a steady current, regardless of the load resistance or voltage drop across the load. This means that the current remains fixed even if the load changes. A CC source automatically adjusts its voltage to ensure that the current remains at the set value.
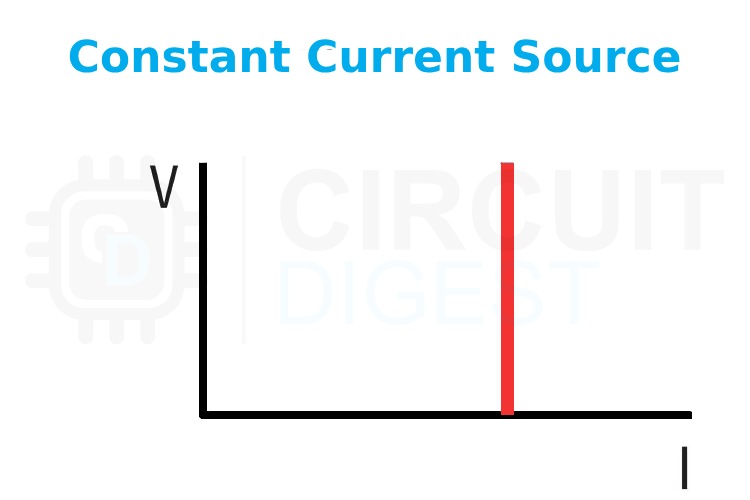
The above image shows the typical graph plotting the output voltage of a constant current source. As you can see the power supply will try to provide a constant current by reducing the output voltage.
Characteristics of Constant Current Source:
- Fixed Output Current: The current supplied by a CC source remains constant.
- Varying Voltage: The voltage adjusts based on the resistance or impedance of the load. If the load changes, the voltage will increase or decrease to maintain the constant current.
- Applications: Constant current sources are critical in applications where a precise current is needed, such as:
- LED Drivers: LEDs are current-sensitive devices that need a constant current for optimal brightness and lifespan.
- Battery Charging (initial stages): In the early stages of charging, many batteries, like lithium-ion, are charged using constant current.
- Electroplating and Electrophoresis: These processes require precise control of the current to ensure quality and consistency.
Example: LED drivers are a classic example of constant current sources. LEDs need a consistent current to maintain a stable brightness and avoid damage. A constant current LED driver adjusts the voltage as the LED’s temperature or electrical characteristics change to keep the current constant.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Ensures precise current delivery, ideal for current-sensitive devices like LEDs.
- Cons: Voltage can fluctuate significantly depending on the load, not ideal for devices that require a stable voltage.
Key Differences Between Constant Current and Constant Voltage Sources
|
Characteristic |
Constant Voltage (CV) |
Constant Current (CC) |
|
Output |
Fixed voltage, variable current |
Fixed current, variable voltage |
|
Load Behavior |
Voltage remains stable, current changes with load |
Current remains stable, voltage changes with load |
|
Typical Applications |
Power supplies for electronics, USB chargers, battery chargers (in the final stage) |
LED drivers, battery chargers (initial stage), electroplating |
|
Primary Function |
Maintaining a steady voltage |
Maintaining a steady current |
Applications in Power Supply Design
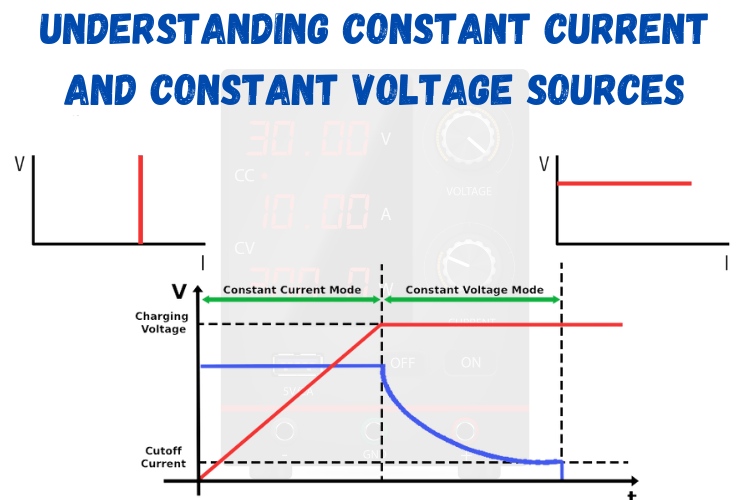
Modern power supplies often integrate both constant voltage and constant current modes, especially in battery charging systems. For instance, many battery chargers start in constant current mode to quickly charge a battery to a certain level and then switch to constant voltage mode to top off the charge without overloading the battery.
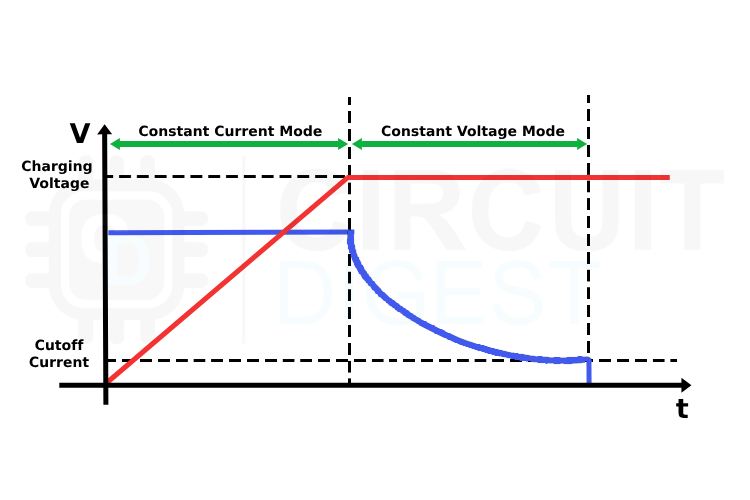
The red colour curve shows the charging voltage, while the blue curve shows the charging current.
In LED drivers, constant current is critical since even small fluctuations in current can affect LED brightness and reduce its lifespan. Similarly, in industrial processes like electroplating, a constant current source ensures uniform deposition of materials, leading to better quality results.








