AHV85003 and AHV85043 isolated SiC gate driver chipsets are optimized for driving discrete SiC FETs
Difference between Microprocessor and Microcontroller

Microcontroller and Microprocessor both terms seem similar but there is a huge difference between these two ICs. Microprocessor only have CPU in the chip like most of the Intel Processors but Microcontroller also have RAM, ROM and other peripherals along with the CPU or processor. Both ICs have different applications and have their own advantages and disadvantages. They can be differentiated in terms of Applications, structure, internal parameters, power consumption, and cost. Let’s see the difference between the microprocessor and microcontroller in detail.
Applications of Microprocessor and Microcontroller
The microprocessor is used in an application where the task is not predefined and it is assigned by the user. It is used in computers, mobiles, video games, TVs, etc where the task is not fixed and it depends on the user. Generally, the microprocessor is used where intensive processing is required. A laptop is the best example where a microprocessor is used. The laptop is used for media streaming, simulation, editing image, web browsing, gaming, creating a document and many more.
The microcontroller is designed for a specific task and once the program is embed on MCU chip, it can’t be altered easily and you may be needed special tools to reburn it. The process of the microcontroller is fixed according to its application. Hence, it does some processing, based on the input given to the microcontroller and gives the predefined results as an output. The input could be given by the user or it could be given by the sensors. It is used in many electronic appliances like washing machine, microwave oven, timer, etc. In these equipments, the process is predefined, it may need some inputs from user to give predefine output. Let say washing machine, once the user sets the input parameters, it wash the clothes according to input parameter. So, the basic task (washing the clothes) for the washing machine is fixed. You cannot do anything else from the washing machine.
Structure of Microprocessor and Microcontroller
The microprocessor is used in the very intensive processes. It only contains a CPU (central processing unit) but there are many other parts needed to work with the CPU to complete a process. These all other parts are connected externally. The microprocessor chip is not containing all these parts internally. The number of external parts and the size of the external parts depends on the application. Generally, it connected with memory elements like RAM and ROM, I/O ports, timers, serial interface, etc. The advantage of the microprocessor is that it has a flexible structure. It means you can decide the size of RAM, ROM, number of I/O ports and can modify all the things which are connected externally according to the application.
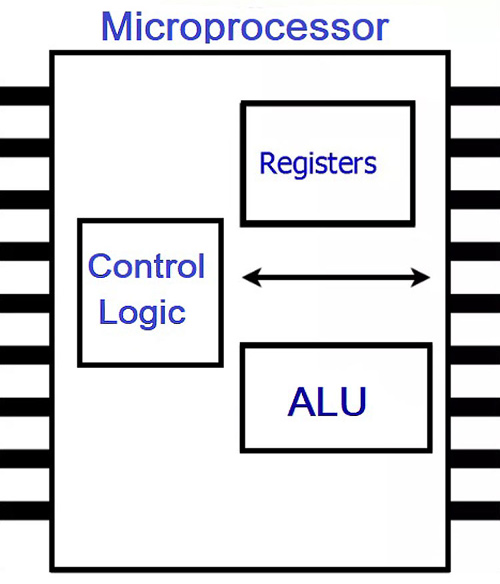
Microcontrollers are used to do the same assigned task repeatedly. Hence, the number of I/O ports and the amount of memory required is less compared to the microprocessor. As told earlier, in microcontroller external parts are integrated with CPU in a single chip and because of this integrated structure the overall size of the microcontroller is smaller compared to the microprocessor. In microcontroller you cannot modify the size of RAM, ROM and other components. Once a controller is designed the structure is fixed. So, the structure of the microcontroller is not flexible.
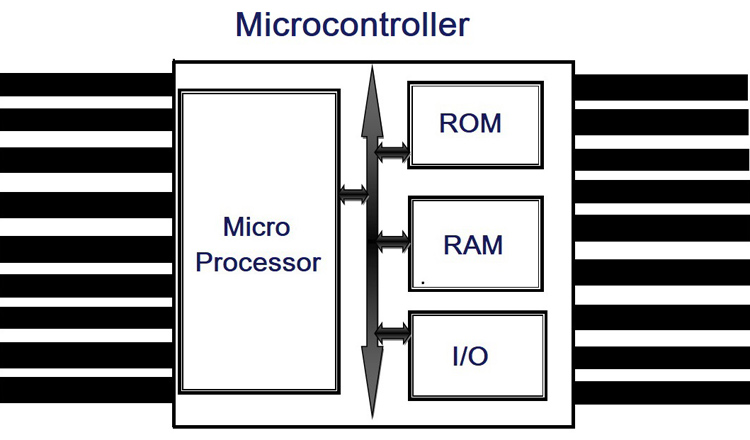
Internal Parameter of Microprocessor and Microcontroller
Both ICs are different in internal parameters like; clock speed, memory (RAM and ROM), peripheral interface, etc. So let's check the important difference between microprocessor and microcontroller ICs in terms of internal parameters.
Clock speed:
The microprocessors are run at higher clock speeds. The clock speed of a microprocessor is in the range of 1 GHz to 4 GHz. While in the case of microcontroller, high clock speed is not required. The clock speed for the microcontroller is in the range of the 1 MHz to 300 MHz.
Memory:

The microprocessors have to run an operating system or it is used for very complicated tasks. Hence, the amount of memory required for the microprocessor is very large. The volatile memory (RAM) for the microprocessor is in the range of the 512 MB to 32 GB. The hard disk (ROM) for the microprocessor is in the range of the 128 GB to 2 TB.
The microcontrollers are designed for a specific task. The amount of memory required for the microcontroller is quite less compared to the microprocessor. The volatile memory (RAM) for the microcontroller is in the range of 2 KB to 256 KB. The hard drive or flash memory (ROM) is in the range of the 32 KB to 2 MB.
Peripheral interface:
The common peripheral interface for the microprocessor is USB, UART, and high-speed Ethernet and the microcontroller peripheral interface is I2C, SPI, and UART.
Programming:
The program for the microprocessor can be changed for different applications. While in the case of the microcontroller once it is designed, the program is common for that application. There is no option for the modification of the program. So, the programming of the microprocessor is difficult compared to the microcontroller.
Bit size:
Modern-day microcontrollers are 32 bit and 64 bit. The 32-bit microprocessor can handle 32-bit binary data at the same time. Hence the address and data bus are 32 bit. Similarly, the 64-bit microprocessor can handle 64-bit binary data at the same time. The microcontrollers are 8 bit, 16 bit or 32 bit. Therefore, the amount of data that can be handled by a microcontroller in a single cycle is lesser compared to the microprocessor.
Power Consumption:
The power consumption for the microprocessor is higher compared to the microcontroller.
Cost of Microprocessor and Microcontroller

Microprocessors are used to perform complex calculations and are used in high end systems like computer, mobile phones etc. Also they generally have more I/O pins than a microcontroller to connect more RAM, ROM and other I/O devices. So generally they are costlier then microcontroller. But its not always true and you can find some microcontroller, which have high end processer, more expensive than a microprocessor.
Summary
Now, let’s summarize difference between the microprocessor and microcontroller in a tabular form.
|
|
Microprocessor |
Microcontroller |
|
Application |
It used where intensive processing is required. It is used in personal computers, laptops, mobiles, video games, etc. |
It used where the task is fixed and predefined. It is used in the washing machine, alarm, etc. |
|
Structure |
It has only the CPU in the chip. Other devices like I/O port, memory, timer is connected externally. The structure of the microprocessor is flexible. Users can decide the amount of memory, the number of I/O port and other peripheral devices. |
CPU, Memory, I/O port and all other devices are connected on the single chip. The structure is fixed. Once it is designed the user cannot change the peripheral devices. |
|
Clock speed |
The clock speed of the microprocessor is high. It is in terms of the GHz. It ranges between 1 GHz to 4 GHz. |
The clock speed of the microcontroller is less. It is in terms of the MHz. it ranges between 1 MHz to 300 MHz. |
|
RAM |
The volatile memory (RAM) for the microprocessor is in the range of the 512 MB to 32 GB. |
The volatile memory (RAM) for the microcontroller is in the range of 2 KB to 256 KB. |
|
ROM |
The hard disk (ROM) for the microprocessor is in the range of the 128 GB to 2 TB. |
The hard drive or flash memory (ROM) is in the range of the 32 KB to 2 MB. |
|
Peripheral interface |
The common peripheral interface for the microprocessor is USB, UART, and high-speed Ethernet. |
The common peripheral interface for the microcontroller is I2C, SPI, and UART. |
|
Programming |
The program for the microprocessor can be changed for different applications. The programming of the microprocessor is difficult compared to the microcontroller. |
The program for the microcontroller is fixed once it is designed. |
|
Bit size |
It is available in 32-Bit and 64-bit. |
It is available in 8-bit, 16-bit, and 36-bit. |
|
Cost |
The cost of the microprocessor is high compared to the microcontroller. |
It is cheaper. |
|
Power consumption |
The power consumption for the microprocessor is high. |
The power consumption for the microcontroller is less. |
|
Size |
The overall size of the system is large. |
The overall size of the system is small. |








