AHV85003 and AHV85043 isolated SiC gate driver chipsets are optimized for driving discrete SiC FETs
Darlington Transistors: An Overview
What is a Darlington Transistor?
A Darlington transistor, or Darlington pair, is a semiconductor device that consists of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) that are connected in a particular manner so that the current amplified by the first transistor is further amplified by the second one. This configuration results in a higher current gain than what could be achieved by a single transistor alone. The Darlington transistor is widely used in electronic circuits for applications requiring high current gain.
Darlington Pair Transistor Circuit
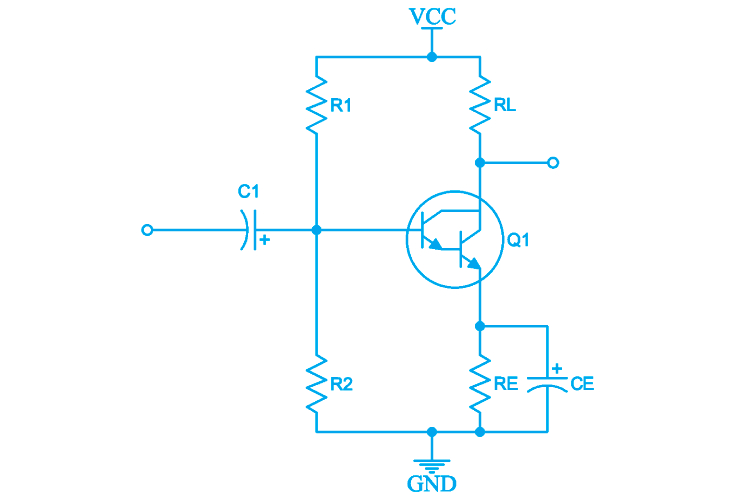
The Darlington pair transistor circuit is a simple configuration where two transistors are connected in such a way that the current gain is significantly increased. In a typical NPN Darlington pair, the collector of the first transistor is connected to the collector of the second, while the emitter of the first is connected to the base of the second. The input signal is applied to the base of the first transistor, and the output is taken from the emitter of the second transistor.
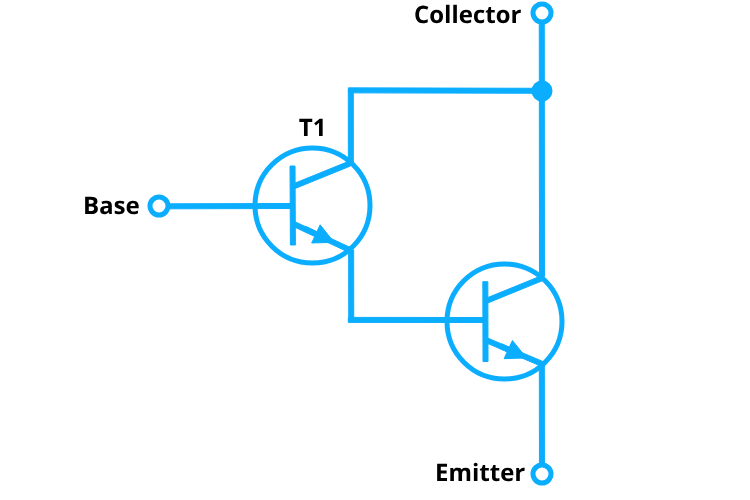
How Does a Darlington Transistor Work?
The Darlington transistor operates by cascading two transistors, typically of the same type (both NPN or both PNP). In this setup, the emitter of the first transistor is connected to the base of the second transistor. When a small input current is applied to the base of the first transistor, it turns on and allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. This emitter current then acts as the base current for the second transistor, which further amplifies the current, resulting in a significantly higher overall current gain.
The Above image shows the typical working of a Darlington pair. Both transistors have a gain of 100. The first transistor receives a base current of 1.51 µA and amplifies it to 151 µA at its collector. This amplified current then serves as the base current for the second transistor, which further amplifies it to 15.1 mA at its collector. The overall current gain of the two transistors combined is the product of their individual gains, resulting in a total effective gain of 10,000 for the pair.
Darlington Transistor Symbol
The symbol of a Darlington transistor resembles two standard transistor symbols placed in series, with the emitter of the first connected to the base of the second. This symbol represents the internal configuration of the two transistors working together as a single unit.
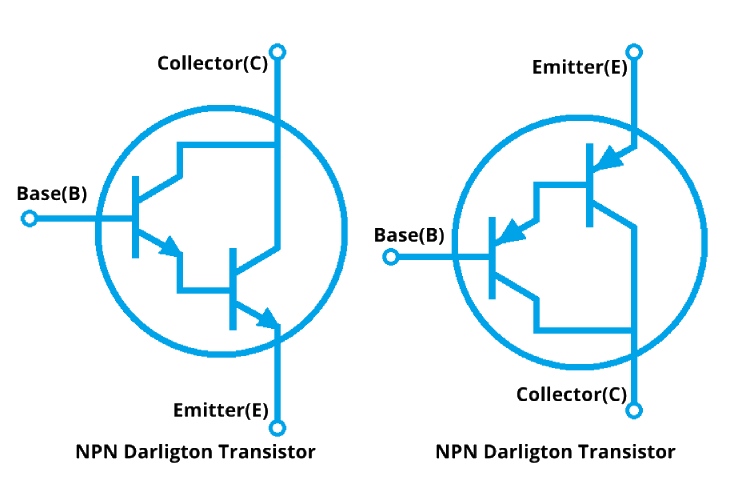
NPN and PNP Types of Darlington Transistors
NPN Darlington Transistor: In this configuration, both transistors in the Darlington pair are NPN type. The NPN Darlington transistor is used in circuits where the load is connected between the emitter and ground, and the collector is connected to a positive voltage supply. Some of the most popular NPN Darlington transistors are TIP120, TIP121, TIP122 and MPSA13.
PNP Darlington Transistor: Similarly, the PNP Darlington transistor consists of two PNP transistors. In this configuration, the load is connected between the collector and ground, and the emitter is connected to a negative voltage supply. PNP Darlingtons are less common but are used in specific applications requiring this configuration. On the PNP side, the most popular Darlington transistors are the TIP125, TIP126, and TIP127.
Darlington Array
A Darlington array is an integrated circuit that contains multiple Darlington transistors in a single package. These arrays are commonly used in applications where multiple loads need to be controlled by a microcontroller or other digital circuits. The ULN2003 is a popular example of a Darlington array, often used to drive relays, motors, and LEDs.
Advantages of Darlington Transistors
- High Current Gain: One of the main advantages of Darlington transistors is their high current gain. The overall gain is the product of the gains of the two individual transistors, which makes Darlington pairs ideal for applications requiring significant current amplification.
- Low Input Current Requirement: Due to the high current gain, the input current required to drive the Darlington transistor is minimal, making it suitable for low-power control circuits.
- Simplified Circuit Design: Using a Darlington transistor can simplify circuit design by reducing the need for additional components to achieve the desired current gain.
Disadvantages of Darlington Transistors
- Saturation Voltage Drop: Darlington transistors have a higher saturation voltage drop compared to single transistors. This is due to the two base-emitter junctions in series, which typically results in a drop of around 1.2V to 2V.
- Slower Switching Speed: The configuration of two transistors in series results in slower switching speeds, which can be a limitation in high-frequency applications.
- Thermal Runaway: Darlington transistors are more prone to thermal runaway, a condition where an increase in temperature leads to increased current, which further raises the temperature, potentially leading to device failure.
Applications of Darlington Transistors
Darlington transistors are used in various applications where high current gain and low input current are required. Some common applications include:
- Power Amplifiers: In audio and other signal amplification circuits, Darlington transistors are used to boost weak signals to drive speakers or other output devices.
- Switching Circuits: They are used in switching applications, such as controlling motors, relays, and lamps, where a small input signal can control a larger load.
- Regulators and Voltage Control Circuits: Darlington transistors are also employed in voltage regulation circuits, where stable output voltage is crucial.
- Darlington Arrays: Integrated Darlington arrays, like the ULN2003, are used to drive multiple loads from a single control signal, often found in microcontroller interfacing.
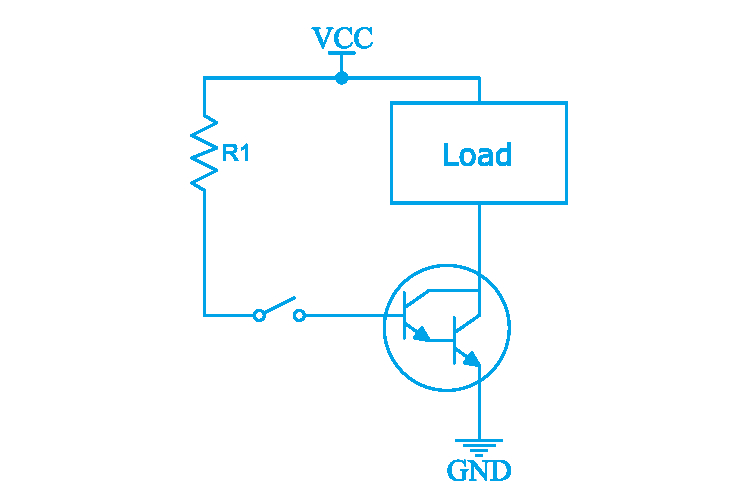
Darlington Transistor as a Switch
In switching applications, the Darlington transistor acts as an electronic switch. When a small base current is applied to the first transistor, it turns on, allowing current to flow through both transistors and turning on the load connected to the emitter of the second transistor. Due to the high current gain, even a small base current is sufficient to switch on large loads.
Darlington Transistor as an Amplifier
As an amplifier, the Darlington transistor is used in circuits where a small input signal needs to be amplified to a much larger output. The high current gain of the Darlington pair makes it suitable for applications like audio amplifiers, where it can amplify weak audio signals to drive speakers or other output devices.