TE Connectivity's UAM Wi-Fi Triple Band Antennas offer a compact alternative for terminal antennas
Different Types of Actuators

Actuators are machines capable of converting a form of energy into physical force or mechanical motions. In easier language, actuators are components that enable motion in a machine or in an object. To perform the motion, actuators need a control signal and a source of energy. The energy can be in the form of electrical energy, hydraulic fluid pressure, pneumatic pressure, etc. The block diagram below shows a simplified action of actuators.

Different Types of Actuators
Actuators can be categorized into 2 types, based on their motion and based on their driving method. In this article, I will be categorizing the actuators on the basis of the input energy required for actuation.
Actuators based on Motion
Based on the motion, actuators can be classified as Linear Actuators or Rotary Actuators.
Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators are machines that provide mechanical force linearly or in simpler words they provide mechanical forces in a straight line, they only have a push and pull motion. The most commonly used linear actuators are push-pull solenoids and hydraulic cylinders which are used in construction equipment. The image below shows a linear electric actuator.
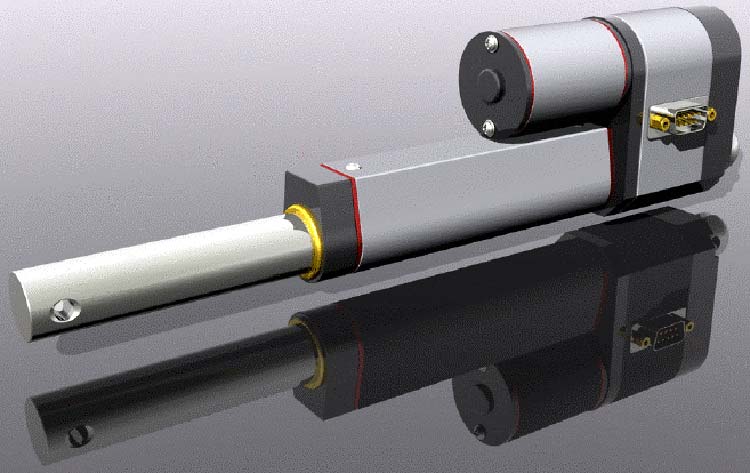
Rotary Actuators
Rotary actuators are able to provide mechanical torque around a point. One of the most common types of rotary actuators is electrical motors. The image below shows a rotary actuator in action.
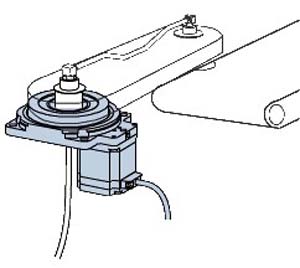
Actuators based on their Input Energy
Actuators are most commonly classified on the basis of input energy. Hydraulic, pneumatic, and electrical actuators are the most common types of actuators present in the market. Hydraulic actuators are the oldest kind of actuators still used while electrical actuators are becoming the most used type. There are new kinds of actuators which are operated by a change in pH level of body or with interaction with certain chemicals, these have their application in the field of Bio-medical and Bio-surgeries which are used
Electrical Actuator
Electric actuators are devices that take electrical energy both AC or DC as an input to provide a mechanical torque or linear motion. Electric motors are becoming one of the most commonly used actuators due to their easier control, longer life spans, and high efficiency. Servo motors and other DC and AC types of motors provide a rotational output. Rotational actuators are the most efficient type of electrical actuator, they have higher power to weight ratio and lower moving parts compared to most linear actuators. The below image shows a rotary actuator used as a valve in a cross-section area of a pipeline.

Electric Linear Actuators
These devices convert electrical energy into linear motion. There are 2 types of linear actuators, one is a solenoid actuator, which provides a linear motion and the second type has a rotary motion with a mechanical system to convert rotary motion into linear motion. These have a motor providing rotating motion and the output shaft is connected to a set of gears and drive mechanism to convert the rotary motion into a linear motion, the output shaft of the linear actuator is connected with the linear guides which ensure proper movement of the output shaft. The second type of linear actuator is most commonly used among the 2 as they have much higher load capacity.
In the image shown below, the left diagram is depicting a solenoid actuator whereas the right figure shows the internals of a linear actuator and its driving mechanism.
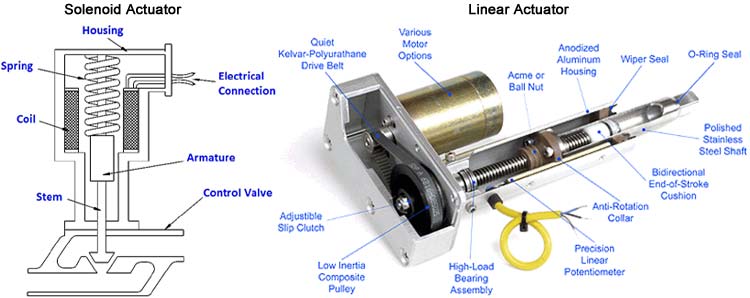
Where are Electrical Linear Actuators used?
Electrical linear actuators are extensively used in industrial applications, they are also commonly used for controlling valves, pumps, etc in power plants, oil and gas plants, etc. In our houses, these are commonly used for solenoid-actuated bell mechanisms, automatic door mechanisms in houses, and find application in electronically operated power windows in cars.
Advantages of Electric Linear Actuators
- Electric actuators offer the highest precision among all types of actuators.
- They are highly modular and scalable for different purposes and force requirements.
- Electric actuators are capable of working in extreme conditions.
- Easy to construct and repair.
- Lack of oil and other fluids make them much more durable for a given weight.
- They produce less sound than hydraulic and pneumatic actuators.
Disadvantages of Electric Linear Actuators
- Higher initial cost for higher powered applications.
- Control mechanism is more complex
- Requires highly skilled people for maintenance and repair.
- These are unsuitable for hazardous and flammable areas.
- Electric motors require a gear mechanism, thus higher maintainability.
Hydraulic Actuator
The hydraulic actuators consist of a cylinder or fluid-based motor which utilizes the power of hydraulics to create mechanical actions. Hydraulic actuators are capable of providing linear as well as rotary motions. They utilize incompressible fluids such as oils from a pump that fills the cylinder to apply power to either one or both sides of the pistons. The speed and force can be adjusted by increasing the pressure of the fluid inside the cylinder. These are the oldest types of actuators known to us. The below image shows a cross-section of the hydraulic actuator. In the image of a JCB machine, we can see 3 hydraulic actuators used to control its arm.

Advantage of Hydraulic Actuators
- They are capable of producing high speed and high power
- Hydraulic actuators can hold constant force even without a pump consuming extra energy for supplying fluids to the cylinder as they utilize incompressible fluids.
Disadvantages of Hydraulic Actuators
- They require higher maintenance cost
- Leaks in the fluid may result in loss of efficiency, the fluids can also impact the environment adversely.
- They are not suitable for extreme temperatures as the fluid property may vary depending on temperatures.
- Hydraulic Actuators have a lot of components such as reservoirs, pumps, release valves, heat exchangers, etc, which can result in lower reliability and higher resources for monitoring, thus increasing the cost of operations.
Where are Hydraulic Actuators used?
Hydraulic actuators are extensively used in industrial applications, they are also used in construction equipment such as JCB machines, diggers, etc for operating their equipment such as plunger or diggers. They are commonly used in brakes of our vehicles or suspension systems etc.
Pneumatic Actuator
Pneumatic Actuators are similar to hydraulic actuators. The difference is the fluid used for driving the pistons is gaseous in nature. The energy is from either a high-pressured compressed air or vacuum is used to get a liner or rotary mechanical motion. Similar to hydraulic actuators, they convert pressure into force. A diagram of air brakes used in trains is shown below
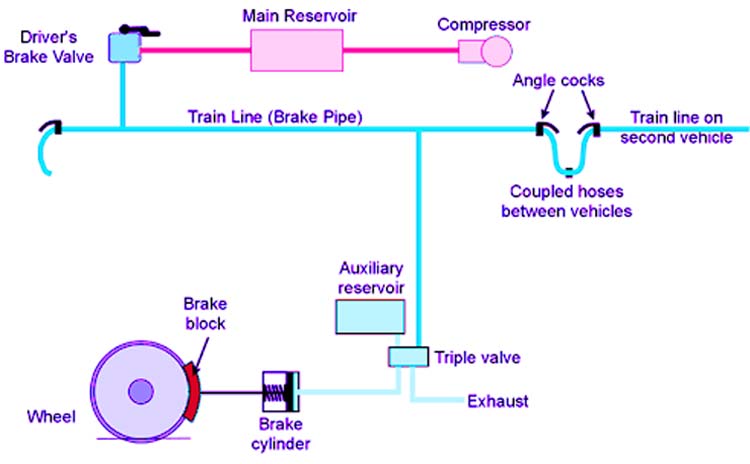
Advantages of Pneumatic Actuators
- Very fast response rate
- High forces can be produced with small pressure changes
- Cheaper to construct and operate than electrical and hydraulic actuators.
- Pneumatic actuators produce higher power than electric or hydraulic actuators.
- It can be used in extreme temperatures and hazardous conditions as it is safer to operate air in hazardous places than chemicals or electricity.
Disadvantages of Pneumatic Actuators
- Even if no movement is required a compressor must operate continuously since pressure losses and compressibility of air make pneumatic actuators loose power.
- Small leaks are difficult to identify than in hydraulic actuators.
- If the air in reservoir gets contaminated by oil, lubrication, or other gases, the power output is changed which leads to downtime and maintenance.
Where are Pneumatic Actuators used?
Pneumatic actuators find applications in a lot of different types of industries, they are used as Rack and Pinion actuators for valve controls operations. They are also used in Pneumatic brakes in vehicles as they are very responsive to small pressure changes applied by the driver.
Magnetic Actuators
Magnetic actuation is based on the Principle of Lorentz Forces, which states that the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a static magnetic field interacts with the static field to produce a force. This force can be used to cause the displacement of a mechanical structure. These are used for very small applications such as nano-robots and have huge potential in the field of bio-medicals. Their main advantage is that they require low voltages and have no contact operations. There is another kind of magnetic actuator known as Magneto Rheological Fluid Actuator. These fluids solidify in presence of a magnetic field and have applications in hydrodynamic bearings, semi-active clutches, etc.
Example: Magnetostrictive micro walker used in biomedical applications, magneto rheological fluid actuator are used as valves, brakes, and dampers.
Mechanical Actuators
Mechanical actuators convert one form of motion into another, they utilize gears, chains, pulleys, rails, and different contraptions for their operations. They are often combined with another actuator and driving mechanism. They are used for increasing torque or power of the output or even to convert linear motion to rotary or vice versa. The gif shows how two rails providing linear motion to the gear are converted to a rotary motion.
Examples: Rack and pinion mechanism, crankshaft in engines, etc.
Thermal Actuators
Thermal actuators are usually made up of metals or shape memory alloys, which can retain a predefined shape when required heat energy is provided. These are thermal-sensitive materials capable of producing linear operations in response to change in heat energy. The main advantages of thermal actuators are compact, light in weight, and easy-to-use devices. The below image shows a thermostatic valve, commonly used in our showers to passively control the temperature of the water.
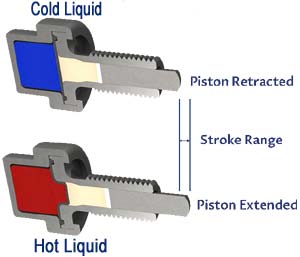
Examples: Thermal actuators are commonly used as temperature control mechanisms in thermostats, electric iron boxes, and as thermostatic valves in pipelines containing fluids, these are frequently used in passive temperature control applications in industries, homes, automobiles, etc.
Soft Actuators
Soft actuators are polymer based actuators designed for very niche operations to perform delicate tasks such as manipulating the internal organs in biomedicine or harvesting fruits in agriculture. Their main advantage is that they have low density and are biodegradable. Based on their composition can respond to stimuli such as light, heat, emf, change in pH, etc.
Application of Soft Actuators
These are commonly used in surgeries and in the field of biomedical they also have applications in the aerospace industry.
Conclusion
All the actuator technologies have their specific application and hence place in the industry. But the most common and flexible types of actuators are hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric actuators. Mechanical actuators are usually used in conjunction with other actuators or drive mechanisms to provide the desired mechanical outputs. The soft actuator is being investigated a lot because of its great potential in the field of biomedical and biochemistry.








