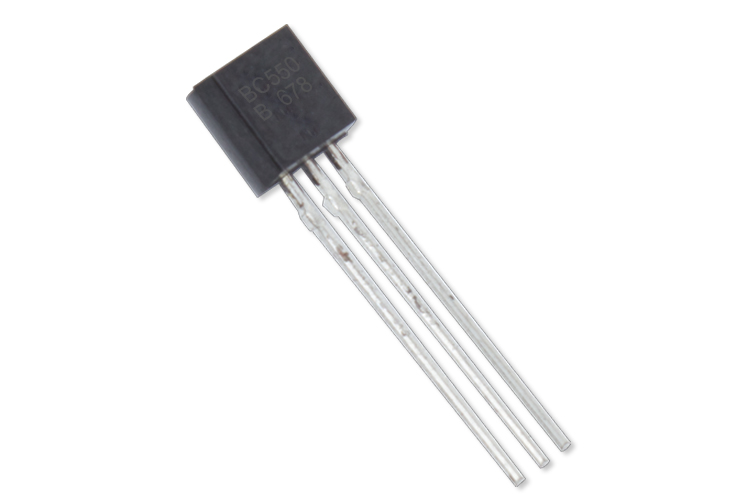
BC550 NPN Transistor
BC550 Pinout Configuration
|
Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|
1 |
Collector |
Electrons Emitted from Emitter Collected by the Collector |
|
2 |
Base |
Controles the biasing of the transistor |
|
3 |
Emiter |
Electrons emitted from the emitter into the first PN junction |
Basic Overview and Features
• Switching and Amplifier
• High−Voltage: BC546, VCEO = 65 V
• Low−Noise: BC550
• Complement to BC556, BC557, BC558, BC559, and BC560
• These are Pb−Free Devices
• Available in TO-92 Package
Note: More technical information can be found in the BC550 datasheet, linked at the bottom of this page.
BC550 Equivalent Transistor
BC547, BC548, BC549, 2n3904, 2SC5200,BC639, BC636, 2N222 TO-92,
Basic Working of a Transistor
The BC550 Transistor is a general purpose N-P-N transistor, in which N-P-N transistor electrons work as the primary charge carriers that are emitted from the emitter of the transistor to the PN junction. When a positive voltage is applied to the base holes are created to the base so they start migrating to the emitter junction,this process thins out the depletion region from PN junction and more and more electrons start flowing to the and all of those electrons are collected by the collector.
General Description of BC550 Transistor
The BC550 is a NPN Transistor, hence we need to provide a small amount of positive voltage to the base of the transistor to turn it on. This transistor comes with three different versions BC550A,BC550B, and BC550C, if you are using this transistor as an amplifier make sure you check the gain of the transistor from the datasheet that can be found down below, because of different versions, the gain value differs which can completely ruin your calculations. The maximum collector current of this transistor is rated at 100mA with an maximum emitter base voltage of 5V. This transistor has a collector emitter voltage of 45V and a collector base voltage of 50V. This transistor can operate with 150*C.
When this transistor is in biased condition, then it can allow a maximum current of 100mA across CE(Collector Emitter) Junction, this state of the transistor is called the saturation state and driving a load that consumes more current than 100mA may damage the device in this condition. As you already may know a transistor is a current controlled device so when base current is removed the transistor becomes fully off, in this stage the transistor is working in its Cut-off Region and the Base Emitter voltage could be around 660 mV.
How to use BC550 Transistor
Unlike MOSFET’s transistors are current controlled devices, meaning they can be turned on or off by supplying required base current, for the BC550 transistor it is 2mA. BC550 is a NPN transistor that means it will be left open when no current is applied to its base, but when we apply a base voltage the
The simulated circuit below shows how this transistor behaves when a base current is applied to the and when no current is provided to the base.
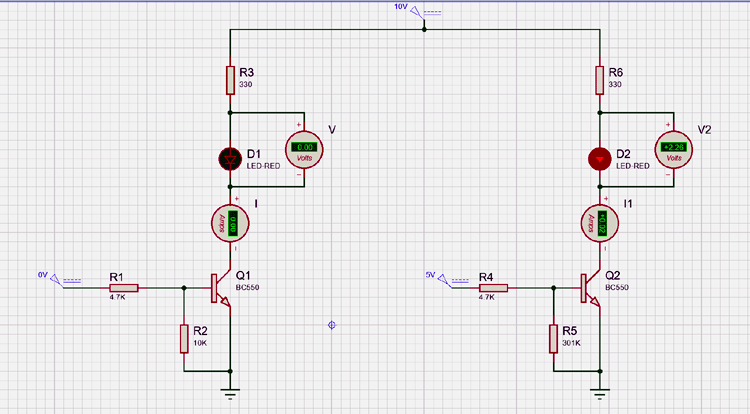
When we turn on the transistor by supplying a required current to the base of the transistor it will remain on unless the voltage at the base of the transistor reaches zero. The base of the transistor cannot be left floating otherwise there could be false triggering to the transistor which may lead to issues in the circuit. To resolve the issue we need to add pulldown resistors for the above example a 10K resistor is used to pull down the base of the transistor.
Applications
- Switching relates and LEds
- PWM driven application
- LED dimmers or flashers
- Switching Applications
- Preamplifier for Power Amplifier
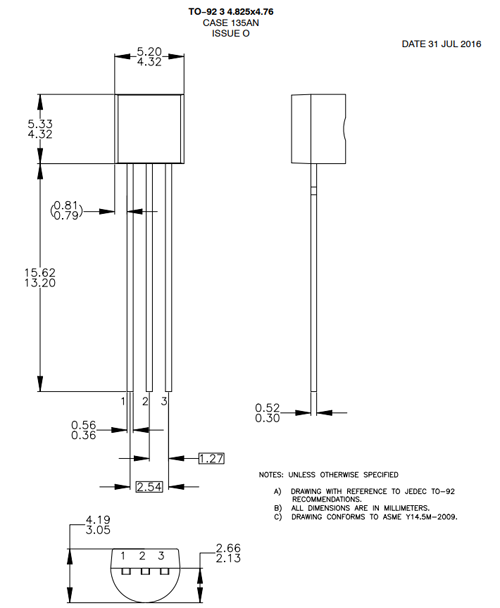
2D Model and Dimensions
If you are designing some projects that require the measurement of the component hear is a quick look at the dimension of the device, more info can be found in the datasheet of the device linked down below.